RAID Log: How is it useful for a Project Manager?
A Project Manager or a Program Manager faces a swarm of challenges. These challenges especially include managing the constraints and making appropriate assumptions. What if, the initial assumptions don’t hold true for the project? Or project risks are not captured well? Or if risks were captured, would you allow them to slip off from the top of your head? What would happen, if you have unresolved issues for long time in a project? What if, the deliverable from any project work is not received, which is necessary for next project work to carry out? Do you have the luxury to delay this scheduled work, because the piece of work started earlier is yet to be completed?
Do you care about these roadblocks and face them often in your projects. Yes of course! These are very obvious hiccups in projects, faced by Project or Program Managers. If they are not identified and handled well in advance, they may lead to project failure.
You may also like: Project Documentation: Does a project really need it?
RAID log equips you to identify, evaluate and monitor Risks, Assumptions, Issues and Dependencies. These are four major components of a RAID log. If you want to take the advantage of this tool in your projects and seek for removing the above hurdles, I would recommend reading this article thoroughly. This literary piece uncovers some of the key answers to the above questions.
What is a RAID Log?
RAID is an acronym, which unfolds into Risks, Assumptions, Issues and Dependencies. RAID log is a single tool, which helps a project or program manager to track the following:
- Risks
- Assumptions
- Issues
- Dependencies
Thus, RAID Log acts as an aide-memoire for a busy project manager.
Risks, Assumptions, Issues and Dependencies are unavoidable challenges in any projects, which requires early identification and action plans or strategies to deal with them, if they occur. Each of the components of RAID is managed through identification, evaluation and action plans with responsibility and due dates.
RAID Log provides a Project Manager with a mechanism or template to record all the four components of RAID as mentioned. This way, she is reminded of the project challenges and prepares herself accordingly.
You may also like: How to create a perfect Project Plan: A step by step guide
Objective of RAID Log
During projects, it’s very essential to capture each of the four components of RAID. Identifying them early in the projects helps us to prepare the strategies and action plans to fix them. Avoiding them may cost us or even may derail the project completely. Thus, to ensure a project success, one should capture these project nuances and never let them slip out of one’s mind. It is not easy and feasible to store the myriad of this overwhelming information in mind. Luckily, RAID log is a place to capture and assess all the RAID components and track their real time status.
Let’s understand the RAID components in detail:
1. Risks: Risk is any event with a level of uncertainty, which if materializes, may impact the project deliverables or outcomes negatively or positively. Risks are identified throughout the project life cycle. For better success rates in projects, a project manager must try to identify negative as well as positive risks and analyze them for severity. Highly severe risks must be attended to mitigate or leverage at the earliest in the projects.
2. Assumptions: Assumptions are the factors, which are assumed to be true in the project. All planning are based on these assumptions, considering them to be valid. However, they are hypothetical based on the best experience, project estimations and historical or present situations. Assumptions hence, may be valid or may not be. If assumptions are invalid, they may have detrimental impact on the project outcome, because project plans are laid down, considering these assumptions are true.
3. Issues: Issues are the current or past events, which require either quick fix or planned strategy to resolve them as soon as possible. Issues, if left unattended or unresolved, may derail the project and create hurdles for project delivery.
4. Dependencies: These are the tasks or events, which are either dependent on the result of some tasks/events or those tasks/events which require outputs. Dependency may be of two types – inbound and outbound. Due care is required to understand dependencies and meet the project delivery requirements. Dependency, if neglected may cost the project highly or might impact the project schedule.
Why should we monitor risks in a project?
Risk is one of the major constraints in a project for a project manager. Risks are the part of any project and may pose obstacles throughout the project life. Risks should be identified at early stage of the project and regularly monitored for their severity. Severity of any risk is defined by the combination of its probability and impact. To reduce the risk severity, one needs to either reduce the risk likelihood of occurrence or reduce its impact or reduce both of these factors. Risks, if not monitored and mitigated, can result in project failure. Projects are likely to witness failure due to negligence in identifying or monitoring risks.
How to use a RAID Log?
RAID log is very simple to use. A simple spreadsheet template to record RAID details would suffice the requirement. However, the most difficult part of RAID log is to identify RAID components. It requires good experience and expertise to identify them. Once identified, the next steps are to evaluate their criticality, actions to reduce their likelihood/ impact and assigning responsibility along with due date. RAID log is a live document, so it should be reviewed periodically. Depending upon the level of criticality, project duration and complexity, review periods can be decided from weekly to fortnightly or higher.
It is recommended to start the use of RAID log in a project from a very initial stage, so that RAID elements can be captured right from early stage of the project. But remember, identifying RAIDs is not only one time activity; you should continuously make efforts to identify all possible and probable RAIDs. Ample amount of focus is required to identify and evaluate RAIDs during initiation and planning of a project, so that the action plans can be laid out for future situations.
However, it does not mean that focus should be diluted during actual execution of the projects. Projects often are characterized by progressive elaboration. That is, we get more and more visibility, when we sail through the project progressively. Assumptions and Dependencies are made known at a very early stage of the project along with initial risks. Though, other risks and issues materialize later in the projects. Hence, as and when you identify any risk or come across any issue, record them in RAID log with appropriate details to mitigate or resolve them.
You may also like: Earned Value Management: What is its significance in Project Management?
RAID Log Sample Templates
As explained in earlier section, you don’t require special software with hefty cost to use RAID logs. A simple excel template can do wonders. RAID logs can be customized templates to capture detailed information regarding RAID. It should typically contain fields to capture the following details:
- RAID item
- It’s description
- Criticality in the project
- Impact and likelihood, as appropriate
- Rank order, to prioritize the actions
- Action plan, with strategies, responsibilities and due date
- Current status of RAID item
A RAID log may contain four worksheets in order – Risk, Assumption, Issue and Dependency. Generic worksheets for each of these RAID items may be created as shown in below figures 1 – 4. However, you can customize these templates as per your needs.
The common fields for these four worksheets here would be, Project name, Last Reviewed Date (Date, when this log was last reviewed), ID (Identification number of this RAID item) and Date Raised (Date, when this RAID item was raised or identified). ID can be classified as:
- R1, R2, R3….. for Risks;
- A1, A2, A3,…… for Assumptions;
- I1, I2, I3,…… for Issues; and
- D1, D2, D3,…… for Dependency.
Risk
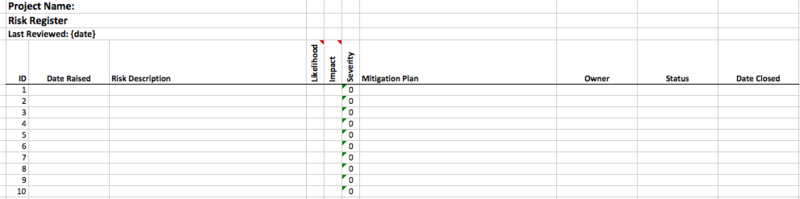
Figure 1: Risk log sample template
Risk log template contains the following fields:
Risk Description: A short description of the identified Risk.
Likelihood: A likelihood rating on a scale of 1 – 5 based on the probability of materialization of the risk. Higher rating is given to high chances of occurrence.
Impact: An impact rating on a scale of 1 – 5 based on the impact of the risk on project outcome. Higher the impact, higher the rating.
Severity: Severity of a risk is nothing but multiplication of Likelihood and Impact ratings for that risk. Severity decides the importance of the risk to mitigate on priority.
Mitigation Plan: Plan or strategy to mitigate the severity of the risk. Strategy may include acceptance, mitigation, transference or avoidance. Remember, risk can be negative or positive. A seasoned project manager not only captures negative risk, but also identifies and tracks positive risks. Positive risks can be leveraged to promote success in the projects.
Owner: Responsibility or ownership is assigned for the risk mitigation plan.
Status: Helps to track the current status of any risk.
Date Closed: Date of closure or resolution.
You may also like: Best Project Management Templates to Ease Up Your Project Work
Assumption
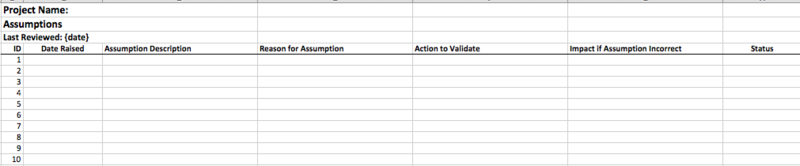
Figure 2: Assumption log sample template
Assumption log template contains the following fields:
Assumption Description: A short description of the initial assumption.
Reason for Assumption: A short note on the reason behind the assumption made.
Action to Validate: List of actions to be performed to validate and ascertain initial assumptions. These actions if validate the assumptions to be true, elevate the project manager’s confidence in decision making.
Impact, if Assumption is incorrect: Evaluate and describe the impact on project, if the initial assumption doesn’t hold true.
Status: Helps to track the current status of any assumption.
Issue
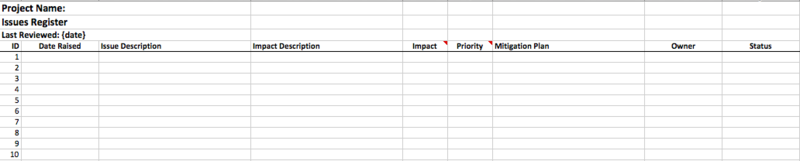
Figure 3: Issue log sample template
Issue log template contains the following fields:
Issue Description: A short description of the current issue.
Impact Description: A short description of the impact on the project due to the current issue.
Impact: An impact rating on a scale of 1 – 5 based on the impact of the issue on project outcome. Higher the impact, higher the rating.
Priority: Based on the impact rating, priority is set. Priority rating decides the importance of the issue to be resolved in order.
Mitigation Plan: Plan or strategy to mitigate the impact of the issue or resolve it. Remember, issues differ from risk. Risks are based on assumptions, while issues are already occurred events requiring attention.
Owner: Responsibility or ownership is assigned.
Status: Helps to track the current status.
Dependency
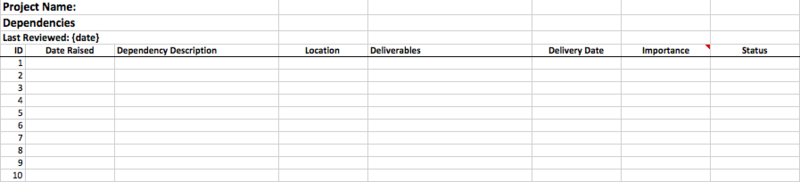
Figure 4: Dependency log sample template
Dependency log template contains the following fields:
Dependency Description: A description of the task or work dependency.
Location: Location suggests, whether it is an inbound or outbound dependency.
Deliverables: Mention the deliverables to be produced or required.
Delivery Date: Expected date of producing the deliverables.
Importance: Importance rating on a scale of High, Medium, Low for the dependency task item.
Status: Helps to track the current status.
Pros and Cons of using a RAID log
Though, RAID log has various pros and aids in the project manager’s work. Yet, it has some cons too. Let’s discuss the pros and cons of RAID log in detail:
Pros related to RAID:
Now that you have understood about so many advantages of using RAID log, you know the various pros. It helps a project manager to record the essential and notice-worthy factors of any project. It provides the interface to collect risks, assumptions, issues, and dependencies at one place and provide ease in monitoring their status. Tracking is not so easy if everything is there in your mind only. But, with RAID log, you’ll have a written log for these important events, then you won’t miss any of them by regular monitoring of the log report.
You may also like: Prioritizing project tasks: 6-step process to avoid getting overwhelmed
Cons related to RAID:
Although the pros of RAID log outweigh the cons, there are still some disadvantages of using RAID log. Excessive dependency on using RAID log may consume most of your time, which is required for actual project work. Detailing of RAID items may overshadow the other project constraints, which may create future hurdles. One of the examples is project schedule overrun, because of engaging yourself into the mitigation of each of the issues and risks. You have to analyze in advance, what information you need and up to what extent you need it from the RAID log. Frequency of the RAID log review is again a wise call you need to take so that it should not impact your project performance per se.
Conclusion
To conclude, RAID log provides the interface to capture and record RAID components. It helps project management professionals to track risks, assumptions, issues and task dependencies in projects. Hence, it gives an aid to a project manager to review project constraints and issues regularly. In fact, RAID log acts as a traffic signal during projects. Just like a traffic light signal, this log indicates the status of the RAID items and sets the future directions and actions.
Mitigate your risks, issues & dependencies | Get PMP certified!
