Firewall
It is a wall of separation between the insecure internet and secure internal network. Firewall monitors incoming and outgoing connections, for various rules and patterns, and filters the connections passing through them.
Types of firewall:
Packet Filtering Firewall:
This type of firewall monitors the TCP packet header at TCP level and looks for the source address, destination address, source port, destination port and the protocol used. Depending on these details they either allow or disallow the packets according to the rules written.
Any Any Any 80 Allow – This rule tells the firewall to allow any packet coming from any source going to any source to the port 80 to be allowed.
Circuit level Firewall:
They operate at the session layer and filter at the connections. Even before the packets are transmitted they look for trusted connections and filter based on those trusted connections.
Application Firewalls:
Otherwise called as Proxy firewall; they act at the application layer, filtering the application level packets. At the proxy, different rules can be given to filter the data. The web servers which are usually accessed by the internet users are placed outside the internal network as proxy servers and all connections can be directed to the proxy; thus, protecting the internal network from outside connections.
Stateful Firewall:
This is the combination of all three firewalls. It operates at the Network Layer, filtering transport level packets, session level connections and application data as well. This has a state table which maintains the status of various connections and a rules table. It also keeps track of sequence numbers to protect against related attacks.
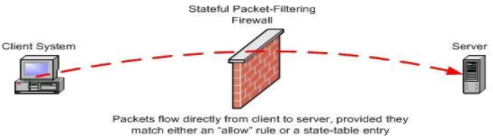
Image Source: http://www.linuxjournal.com/article/7296
Evading Firewall:
-
Using Fragmented Packets.
-
Using Firewalking to scan beyond the firewall for open ports.
-
Using Source routing, avoiding the route of Firewall.
-
HTTP-tunnelling and ICMP-tunnelling.