An Introduction to Quality Control And Quality Assurance
When the Japanese firms penetrated the western markets in the 1970s and 1980s - everyone was taken by surprise. The competing manufacturers wondered how their Japanese counterparts were so successful. They knew why - the Japanese products were of far superior quality. Exactly as to how they pulled it off, was a mystery.
The Japanese manufacturing firm’s success was due to a quality revolution.
They established a quality assurance system by promoting total quality management. Also, they built an organization-wide system to develop tools, techniques, skills, and mindset.
Quality is challenging to objectively define and largely depends on the perception of the customer. Thus, a working definition of quality is “conformance to the specifications” given by the customer. Here, the quality of products and services is a key competitive factor.
If you want to satisfy the needs and expectations of your customers, provide them with high-quality products. You’ll improve customer loyalty, repeat purchases, up-sell, and advocacy.
History of Quality
A good quality management program consists of quality improvement, control, and assurance. So, the quality management standard has gone through revisions, with emphasis on different aspects as it progressed.
The year 2000 saw the revision of the ISO 9000 standard to increase emphasis on customer satisfaction.
In 2015, the revision of ISO 9001 standard increased emphasis on risk management.
Six Sigma, a method developed by the Motorola company, helps improve business processes by minimizing defects. It evolved into an organizational approach that achieved breakthroughs and significant bottom-line results.
Quality has moved beyond the manufacturing sector into service, healthcare, education, and government.
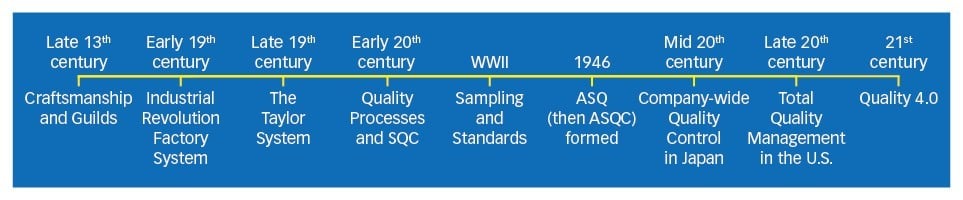
The history of quality dates way back to medieval times. From the evolution of quality in the image above, you can see that quality management has a major role in the industry. Quality improves the goods you sell, as well as production processes and efficiency.
What is Quality Control (QC)?
Quality control guarantees the conformity of items or services through inspections and tests. Here, a quality examiner uses statistical sampling and analysis to test the output. The output could be the end-product manufactured or the service provided.
The aim is to ensure that the result meets the benchmarks set up to approve or disapprove the output on the basis of quality.
The activities that control the quality of products are usually voluntary in an organization. In order for quality control to be adhered to, a slew of activities is monitored. The production processes, the storage, and even transportation. This is because these activities have a direct impact on the output’s quality.
Quality the state and government guidelines sometimes make it mandatory for businesses to maintain quality control records.
Quality Control Circle
Quality Circle (or quality control circle) is made up of a group of people who identify, analyze, and solve defects and problems. They make use of seven tools that help in quality control. Here is a list of the seven quality circle tools : -
1. Checklists
Quality Control requires you to make a checklist that contains items that are crucial to the product. Then, check each item once you’ve taken action.
2. Fish-bone diagram
This visual tool helps you determine the causes of a problem.
3. Control chart
The control chart shows historical change using specific parameters. The chart helps find and correct problems as they happen. It also helps predict a range of outcomes and analyze variations.
4. Stratification
Stratification separates data to identify patterns and specific problem areas. It avoids a holistic approach to problem-solving.
5. Pareto chart
This is a bar chart that provides a visual analysis of problems and causes. It helps to focus on the most significant issues.
6. Histogram
It is a common graph that uses bars. It identifies frequency distributions that show the number of defects.
7. Scatter Diagram
It is a graph that helps plot info along two axes. It helps visualize the relationships between variables.
Quality control inspectors use one or more of these tools to analyze products or services. From the results, they determine the necessary areas for improvements. An inspector gets training to know what method to use based on the context and how to use it.
Quality Control Today
Quality control started with the rise of manufacturing during the industrial revolution. Factories had to deliver a product that was better than the competitors to draw in customers. But now, it has become a key aspect of the manufacturing industry.
With QC’s evolution, manufacturers have to stay up-to-date with the standards for product quality and safety.
Many companies now produce goods offshore. This trend has increased factory QC inspections. It has also led to an increase in national and professional regulatory bodies to ensure the quality of products. Examples include Europe’s Directorate-General for Health and Food Safety and the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
What is Quality Assurance (QA)?
Quality Assurance prevents mistakes and defects in products and helps in avoiding problems during the delivery of products or services to customers. With this process, organizations create and deliver products that meet customer expectations. Quality Assurance sets up and maintains necessities for developing and manufacturing products.
A quality assurance system intends to build and maintain an organization’s credibility and trust with the customer base. It also improves work procedures and effectiveness that empowers an organization to better compete with others.
The ISO (International Organization for Standardization) is the main force behind QA practices as it maps the procedures that ensure its success. ISO 9000 says Quality assurance is part of quality management, so organizations use it to guarantee that their quality assurance system is effective. Hence you measure QA against ISO 9000 worldwide standard.
QA standards undergo constant updates to stay relevant to today’s businesses. And it focuses on providing confidence in the organization’s ability to meet quality requirements.
ISO 9001:2015, which is the latest revision of the ISO 9000 series, includes improvements to its structure and information for risk-based decision-making. Its features include:
-
Stronger customer focus
-
Top management practices and how they affect a company
-
Keeping up with continuing improvements.
Methods of Quality Assurance
Quality assurance utilizes one or more of these three methods:
1. Failure testing
You use failure testing to determine if a product breaks or fails. For physical products, this may be under heat, pressure, or vibration. Failure tests for software products may be placing the software under high usage or load.
2. Statistical process control (SPC)
It is a method based on data and analysis. This method uses statistical methods to manage and control the production of products.
3. Total quality management (TQM)
TQM applies quantitative methods as the basis for continuous improvement. It relies on facts, data, and analysis. And it supports product planning and performance reviews.
Quality Assurance uses by Industry
Manufacturing
The manufacturing industry formalized quality assurance discipline. Manufacturers ensure that products met the defined specifications and requirements and were without defects.
Food production
Food production uses certain techniques to detect physical contaminants in the food production process. The systems ensure that contaminants are removed and eliminated before products leave the factory.
Pharmaceutical
Pharmaceutical companies employ different quality assurance approaches during each stage of a drug’s development. Example include
-
Reviewing documents
-
Approving equipment calibration
-
Reviewing training records, and
-
Reviewing manufacturing records.
Quality Assurance vs. testing
QA is different from testing because it focuses on processes and procedures, while testing focuses on the usability of a product. So, QA defines the standards for testing, while testing helps in identifying issues.
The testing will ensure that a product meets defined business requirements. Hence, it involves a more tactical process of validating the function of a product.
Quality Control (QC) vs. Quality Assurance (QA)
Some people often confuse quality assurance with quality control. Although the two concepts share similarities, there are important distinctions between them.
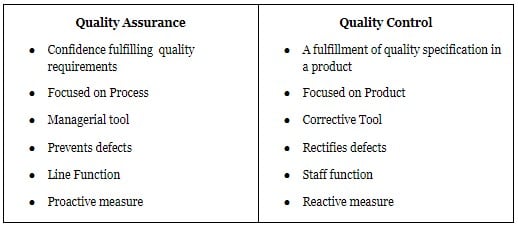
Quality Control verifies the output or product while quality Assurance checks on the quality of the process that produces the product.
The scope and focus areas of QA and QC are also different. Quality control focuses on identifying and correcting the defects in the finished products, so it is a reactive process. But, quality assurance aims to prevent defects from occurring. So, it is a proactive approach. It focuses on process performance, which produces the product.
Their goals differ as QC’s is to identify defects after the product developed and before its delivery. But QA’s goal is to improve development and testing processes, and the defects do not arise when the product is being developed.
QA and QC also have different approaches to achieve their goals. QC finds and eliminates the source of detected quality problems through tools and equipment. Whereas, QA establishes a good quality management system and assessment of its adequacy.
QA performs a periodic conformance audit on the system to ensure that everything is in place, as per the organization design.
Each function needs someone to be responsible for it. For QC, a dedicated team to perform analysis and inspection. But QA is the responsibility of everyone involved in its product development.
Examples of quality assurance are process checklist and project audits. QC helps verify that the deliverables are within the specifications required by the customer. You can use QC’s tools for inspection, peer reviews, and the testing process.
Both QA and QC use statistical techniques, but the purpose is different.
Summary
Quality Assurance provides a complete guideline to use in any industry. Following this process ensures that your products meet the specified requirements.
Quality Control, on the other hand, is a product-focused process that addresses other issues, such as individual inspections or defects.
What’s next? Become a Quality Expert. Register now!