Project Management Decoded: From Certifications to Careers
Perhaps you are running after the title of Project Manager. But you aren’t far away from realizing that it’s the power of purpose that drives projects. The latest data from the 2020 Pulse of the Profession® report shows that 11.4% of investment is wasted because of poor project performance. This is what happens when a project is not rooted in a purpose. That’s why future-fit organizations are eyeing for project professionals who are aware of progress assessment, have the technical know-how of reviewing deliverables, and can lead cross-functional teams without being dependent on other business areas. In fact, the project-oriented labor force in sectors like manufacturing, information services, finance, utilities, oil and gas, and professional services is set to grow by 33% through 2027. Also, organizations are shifting towards onboarding individuals who can manage, lead, and execute projects instead of hiring people with specific job descriptions.
Now that you’re aware of the project management job scenario, the question is - are you ready to pitch your project management abilities to your current or future employer? From getting certified in project management to building your own project management portfolio - the path is long and full of surprises. This project management career guide is designed to help you navigate the uncharted waters and get your foot in the door.
What Is Project Management?
Before delving deeper into what project management entails, let’s take a minute to understand what a project is. A project is an endeavor that is created to deliver results with resources available within a fixed timeframe. It has a singular goal and may involve teams across organizations and geographies. For example, developing a software or building a bridge, or expanding global footprint - all of these are projects. Every project has three elements at its core:
- Time: The timeline is an important element of a project since it gives a clear picture of what work needs to be complete by when.
- Cost: Costing gives an idea of whether or not funds are required for completing a project on time and how to manage finances.
- Quality: Quality assessment helps in understanding if the deliverables meet the standard of the deliverables agreed upon at the beginning.
Project management involves applying skills, tools, and techniques for the purpose of meeting project requirements within the defined timeline and budget. While management can be an ongoing process, project management involves a final deliverable. This is why it is best for project management professionals to be aware of business trends and possess technical as well as people management skills.
According to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK) by the Project, project management processes include initiation, planning, execution, monitoring, controlling, and closing. Experience in areas such as integration, human resources, quality, risk management, cost, time, stakeholder management, etc. lies at the heart of project management success.
The Association for Project Management considers the followings as the core components of project management:
- Why: The first and foremost step is to define the need for a project.
- Project Requirements: Understanding project requirements along with quality of deliverables helps you in determining the timeline and resources required.
- Business Case: A business case aids you in justifying the investment you are looking for and securing funding.
- Project Plan: The next step is to develop and implement the project management plan while keeping the project delivery team motivated at all times.
- Risk Management: Now it is time to monitor the project progress and manage risks along with issues that may come up during the project.
- Budget: Efficient project management involves budget management and requires effective communication with the stakeholders.
- Closing: The final step of project management is closing the project in a controlled environment.
.jpg)
Traditional Project Management (Source: CoSchedule)
Project Management Principles
Project management principles are fundamental rules that are followed in pursuit of successfully completing a project. While the PMBOK Guide by the PMI doesn’t have a list of principles that you should be following for efficient project management, here is a list highlighted in the annual Pulse Survey by the PMI.
1) Formal Project Management Structure: It can be a daunting task to manage and control a project without a structure in place. That’s why it is crucial to have a formalized structure along with a project charter and plan. All of these help you to provide a project with the attention it deserves.
2) Engaged Project Sponsor: An engaged project sponsor is key to project success. In fact, sponsors play an important role in reducing bottlenecks and eventually become the spokesperson of the project. Be it escalating issues for a quick resolution or communicating progress to other stakeholders, the role of a sponsor is indispensable.
3) Clear Goals & Outcomes: At the onset of the project, you should have access to project requirements and approval criteria as well. Having both of these helps you in achieving the desired outcomes. Successful project managers ensure that the goals and outcomes are reviewed and approved by the stakeholders.
4) Role & Responsibility Documentation: Maintaining clear documentation of roles and responsibilities helps you to set expectations among the team members. Project management teams usually use two forms to document everyone’s involvement.
- RACI: Responsible (R), Accountable (A), Consulted (C), Involved (I).
- RASCI: Responsible (R), Accountable (A), Sign-off Authority (S), Consulted (C), Involved (I).
.jpg)
An illustration of the RACI Matrix
A RACI matrix contains team members and tasks. Usually, the team members are listed along the top and tasks along the sides. Each member in your team will be assigned a letter from R, A, C, and I, depending on their role in the project.
5) Change Management: It might happen that the stakeholders want additional features to be added. This is known as scope creep and refers to the situation when a project goes beyond the initially agreed upon guidelines. That’s why project management professionals need to have strong change management skills.
6) Risk Management: A risk is an unexpected event that has the potential to impact the project outcomes. Be it processes or resources, everything can be affected by a risk. This is the reason risk management is of utmost importance in project management. Risk management can be divided into identifying and evaluating risks, monitoring them, and implementing action plans.
7) Capability To Deliver Value: Project management professionals depend on processes, tools, and procedures to deliver value to the customers. For example, you may adopt an agile project methodology to ensure project success. Previous experience in delivering successful projects helps you to deploy approaches that are already tested.
8) Performance Management Baseline: Performance Management Baseline refers to integrating plans for three components i.e. cost, schedule, and scope. When one of these plans changes, you will be able to track its impact on the two other elements. This helps you to have a holistic picture and makes it easier for you to make decisions.
9) Communication: They say 90% project management is actually communication. Be it risks, project status, or activities, project management professionals need to communicate well. Effective communication is key to resolving conflicts and making decisions while keeping the stakeholders engaged.
16 Project Management Methodologies
Did you know that the PMBOK by PMI recognizes 47 project management processes? Before knowing more about different project management methodologies, let’s have a look at the knowledge areas that are at the core of these methodologies.
- Project Communication Management: Information dissemination among stakeholders and team members.
- Project Cost Management: Processes that involve funding, budgets, and spending allocation.
- Project Human Resources Management: Team management along with role assignment, hiring, and sourcing.
- Project Integration Management: Processes aimed at defining and consolidating all processes and activities.
- Project Procurement Management: Processes that involve planning and budgeting along with purchasing resources.
- Project Quality Management: Processes designed to evaluate and maintain quality at every stage of the project lifecycle.
- Project Risk Management: Preparation for handling unexpected risks.
- Project Scope Management: Processes that ensure the project requirements are within the scope of the project.
- Project Stakeholder Management: Managing and collaborating with stakeholders whom the project impacts.
- Project Time Management: Processes utilized for ensuring project completion on time.
Each project is unique and requires project managers to adopt a project management methodology. Each of these methodologies come with a unique workflow and process. Here are some of the most popular project management methodologies used by project management professionals across the globe.
1) Waterfall Project Management Methodology
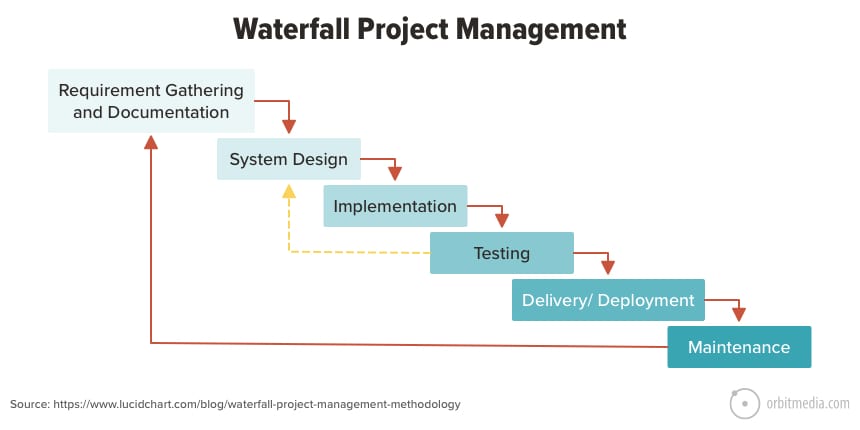
Waterfall Project Management (Source: Orbit Media Studio)
This traditional method of managing projects involves a linear process made of several phases. When you adopt this methodology, you can’t begin a phase without completing the one prior to it. The flow of the project is one-directional like a waterfall and hence the name. It may be a simple methodology but you will need to have everything planned in sequence for project success. Waterfall methodology is not really flexible when it comes to accommodating the needs or priorities of customers.
2) Scrum
Scrum is one of the most popular agile project management methodologies used worldwide. Designed to help developers solve complex problems such as shifting production schedule, convoluted development cycle, etc., this method is comparatively easy to implement. Scrum models are usually run by scrum masters who focus on helping team members navigate obstacles in an efficient manner. Scrums consist of sprints which run for 2 weeks and involve daily discussion among team members on what needs to be done and how.

Daily Scrum Meet Rules
3) Critical Path Method (CPM)
Developed in the 1950s, this project management methodology focuses on plotting the critical path. The idea that lies at the heart of this method is the concept that you can’t initiate some tasks as these are dependent on the completion of a previous one. The critical path is the one you create by combining all these dependent tasks throughout the project. Focusing on this critical path is crucial for prioritizing and allocating resources so that the most important tasks are done on time. This methodology also allows you to reschedule tasks with lower priority so that you can optimize the work process and deliver the end results on time.
4) Kanban
Kanban is another agile methodology that has actually originated from the Toyota factories in the 1940s. Back then, departments used a visual system of cards to communicate their ability to take up more raw materials for production. The methodology today has been modified to facilitate visual representation of ongoing tasks. Project teams can move the ongoing tasks to predetermined stages so that all the stakeholders are able to understand the bottlenecks and track progress.
5) Extreme Programming (XP)
This method was originally developed to improve the ability of developers to adapt and work around the needs and requirements of customers. It relies on short work sprints along with collaboration with stakeholders and frequent interactions - both of which help in improving the quality of the final deliverables. This project management methodology is flexible in terms of task replacements.
6) Adaptive Project Framework (APF)
This project management framework was developed to accommodate the changing requirements of the IT projects. It requires you to create a Requirements Breakdown Structure (RBS) at the beginning of the project so that you are clear about product requirements and features. Iterative stages at the end of each stage helps you to analyze previous results and improve performance. This method provides stakeholders with flexibility meaning that they can change the project scope at the onset of each stage.
7) Lean
Lean methodology is designed to streamline tasks and reduce waste. When you adopt this methodology, you will be creating a work process at the beginning of the project. This will help you to identify possible delays, bottlenecks, and any form of waste. Doing more with less lies at the heart is at the heart of this method. The entire idea evolves around delivering values with less money and less resources in less time.
8) Event Chain Methodology (ECM)
Event Chain Methodology assumes that there are potential risks which are usually not there in the project scope. That’s why project management professionals need to be prepared to handle these risks that can affect project schedule and deliverables along with project success. Basically, you’ll have to stay prepared for addressing risks that may occur.
9) Six Sigma
This methodology heavily relies on statistics for the purpose of process improvement. It does so by measuring and eliminating bugs and defects within a process. So, it is possible for a process to attain a six sigma rating of 99.99% and to deliver a defect-free outcome.
10) Extreme Project Management (XPM)
This project management method is exactly opposite to the waterfall model. With this methodology, you’ll be able to manage changes and still complete a project on time. It allows you to make changes to the plan, budget, and the final deliverable as well, irrespective of the stage the product is in. XPM methodology is suitable for projects that run for a shorter duration.
11) Lean Six Sigma
Lean Six Sigma combines the no-waste approach of Lean and zero-defect vision of Six Sigma. This project management methodology is designed to help you reduce waste to zero as you run cost-effective projects and meet customer demands.
12) Process-Based Project Management
This method is designed to align the project objectives with the larger mission and values of an organization.This allows project managers to create strategic tasks and set goals that are in alignment with the large objectives. It starts with defining a process followed by metrics establishment. Furthermore, it involves measuring processes, adjusting objectives, and improvement planning/implementation.
13) PRINCE2
This methodology has a product-based approach at its core and is used by the UK government for the purpose of managing projects. It uses a structured project board for the purpose of segregating high-level tasks such as resource application, business justification, etc. Project managers are usually in charge of day-to-day tasks like scheduling. Deploying this method allows organizations to use resources in controlled fashion and reduce risks as well.
.jpg)
Prince 2 Themes (Source: Knowledge Train)
14) PRiSM
PRiSm stands for Projects Integrating Sustainable Methods. This methodology helps organizations to incorporate environmental sustainability and manage change at the same time. The entire idea in this method evolves around completing projects while keeping the negative social and environmental impact to a minimum level.
15) The PMBOK Method
It is debatable whether there is truly a project management methodology known as the PMBOK method. But many organizations use the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK) to manage projects. This method consists of five stages i.e initiation, planning, execution, controlling, and closing. While this may not be an official methodology, it is widely accepted by project management professionals around the world.
16) Benefits Realization
This methodology is designed to evaluate whether or not the final deliverable is able to satisfy the customer benefits. Be it conception or execution, this method is all about delivering value to customers as well as stakeholders.
Why Choose Project Management As A Career Path?
The growing profession of project management comes with endless opportunities. Be it a new product or business expansion, businesses across the globe often consider new initiatives as projects. Project managers are responsible for transforming ideas into reality and therefore ensuring project success. So, how do you know if project management is the right career path for you? If you want to be responsible for the final deliverable, are interested in managing cross-functional teams, and are willing to nurture leadership skills, project management is certainly the career path you should go on.
1) Continuous Improvement: As a project manager, you get to work with a different set of teams and stakeholders, both of which change with the project. Every project will teach you something irrespective of the amount of experience you come with. Be it dealing with stakeholders or managing unexpected risks, you’ll have to find a rhythm and get things done in a systematic way. And, this brings in the opportunity for you to learn every day.
2) Career Progression: Want to climb up the corporate ladder? Project management comes with an excellent opportunity for you to expand skills, handle complex projects, and become an expert. You may start your career as a project coordinator and transition into roles that actually require you to manage projects and portfolios. In addition, you’ll always have the flexibility to specialize in areas such as scheduling or allocation.
3) Unique Undertaking: Every project is unique and requires project management professionals to adopt a new approach. Because of their unique nature, projects come with different requirements. In order to fulfill these, your strategic initiative will vary, depending on the project you are working on. This allows you to be unique in your approach every time you manage a project.
4) Knowledge Expansion: Managing projects is all about continuously interacting with team members and adopting strategies for delivering the best results. No matter what certification you have completed, every project will come with the opportunity for you to pick up new skills and expand your understanding of the industries you are catering to.
5) Positive Contribution: Most of the jobs allow individuals to contribute but the stakes are higher when it comes to project management. It requires you to be on track and deliver the final product within budget. As you ensure all these, you will be able to help the organization improve its efficiency as well as performance. The ability to make a positive impact on the organizational performance and the people around is what drives professionals to opt for a career in project management.
What Does A Project Manager Do?
Project management is all about bringing complex projects to life and shaping the trajectory of an organization. Project managers are responsible for on-time completion of projects within budget along with planning, organization, and direction. The ultimate aim is to increase efficiency and revenue while reducing costs. A project manager leads an entire project across the project life cycle which consists of five stages initiation, planning, execution, control, and completion.
As a project manager, you will be working closely with stakeholders and members from different teams. This is why you will have to adapt to different environments, cultures, and people from time to time meaning flexibility is key to success. Successful project managers across the globe are excellent co-workers, leaders, and supervisors. A career in project management means every day will have a new set of challenges and you will be the one responsible for solving potential problems.
Depending on the industry you choose to work in, you will be involved with:
- Directing different phases of project management
- Managing project expectations with stakeholders
- Tracking project progress and coordinating throughout the project lifecycle
- Supervising team members
- Defining project scope and prioritizing tasks
- Updating the project documentation
- Creating forecasts for resource requirements and revenue
- Maintaining daily time sheets
- Ensuring that the tasks complete meet the predefined project scope
- Escalating issues to the management, when necessary
- Managing budgets, billings, and projects with KPIs
- Acting as the main point of contact for customers
- Implementing customer inputs
- Measuring project performance with different tools and systems
- Evaluating team performance from time to time
Project Management Skills
A career in project management comes with regular challenges. That’s why knowledge of project management alone isn’t sufficient. In order to excel in a project management career, you need to be flexible, accountable, risk-taking, and decisive. In addition, you should be able to think strategically and do multi-tasking. While you may not need strong technical skills, general business knowledge is highly important. Another important project management skill is the ability to allocate resources. You should be able to understand the amount of time a resource needs to complete his or her task. Ability to solve problems is equally important when it comes to project management. You should be able to identify issues and suggest solutions on spot. Since a great portion of project management involves teamwork, you should have adequate knowledge of people management, general management processes, and frameworks.
.jpg)
Project Management Essential Soft Skills (Source: Leadership Champs)
Here are some of the most common skills that you should have as a project manager:
- Strong understanding of risk manage processes
- Solid grasp on business cases
- Project management and team management skills
- Communication and leadership skills
- Ability to control and monitor budgets
- Decision-making skills
- Data documentation and ability to draw conclusions
- Ability to interpret instructions
- Multitasking skills along with a creative mindset
- Analytical and time management skills
- Problem solving skills
- Knowledge of project management tools
Designations & Salaries In Project Management
There was a time when project management used to be considered as a hermetic profession. Today the word project applies to all the industries across the world. Whether you are in construction or marketing or manufacturing, industries have different ongoing projects at all times. The growth of the profession has led to an increasing demand for project managers. In fact, there will be a demand for 87.7 million project managers by 2027.
No matter what industry you are in, there will be a hierarchy for project management professionals. Some of the most common designations in the field of project management are:
Project Coordinator: This entry level position is administrative in nature. As a project coordinator, you will be responsible for generating and distributing reports among stakeholders and team members. In addition, you will be supporting the management team as well.
Project Scheduler: A project scheduler plays an important role in large projects. H