Key Principles of Resource Management
Project management as we know has evolved as an important part in most of the organizations. Starting from research and development to big transformations, project management finds its application. But the hard truth is that not all projects become successful as others. If project deliverables and benefits are realized as budgeted and scheduled, the project is entitled as successful. But it’s not as simple as it seems to be.
Unlike the traditional approach, project management is not only about scheduling the project tasks. It also depends upon, how you manage resources well suited to organizational maturity at Project portfolio management (PPM) scale. Resources are very significant, if not primary, components of project management. And if these resources are not properly assigned to the projects, they may lead to project failure being counterproductive. So resource management is essential for an organization practicing project management approaches.
In this article, you’ll learn to define:
-
resource management,
-
resource management methods and
-
resource management importance.
What are management resources required for a project?
Type of resources in the project:
Resources in a project can be -
-
work resources,
-
material resources and
-
cost resources
These resources comprise the people, equipment, facility, knowledge, information (IT), funding or others. They are the key factors for the completion of any project activity. People resources are very important element of any project and not easy to manage. Thus people need some additional ways of dealing when it comes to resource management. They can be made more productive by following some key management principles (discussed later in this article). Now, let’s understand, what Resource management is.
What is Resource management?
The purpose of project management is to collaborate processes, resources and PM tools to achieve a common goal and produce intended deliverables. Hence, apart from project management tools, resources play a vital role for any project success.
Let’s uncover the question - what is resource management? – Its about, how do you manage resources. Hence, resource management is to maximize the resource productivity towards desired outcomes by managing them effectively.
What is project resource management?
“Project Resource management is to effectively use right type of resource for right time during a project execution to produce expected deliverables.” In order to achieve strategic business goals and financial goals, it is desired to maximize the return on investment in resources. Especially with people, because human resources are significant cost element in any project. All projects need people resources with some specific set of skills to accomplish project tasks.
Lets define resource manager role in a project:
Project resource manager is responsible to divide right skills for right project tasks at right time.
Usually, a project manager and resource manager have specific responsibility to carry out any project. Project manager is responsible to plan and execute the project. Resource manager manages between resource demand and supply. He evaluates the resource requirement for a project and assign appropriate resources to project tasks. He or she also manages resource utilization to maximize its productivity. They also analyze necessary metrics related to resource assignment and capacity planning. Below figure 1, well describes the roles of these two.
Figure 1: Roles & responsibilities of project manager and resource manager
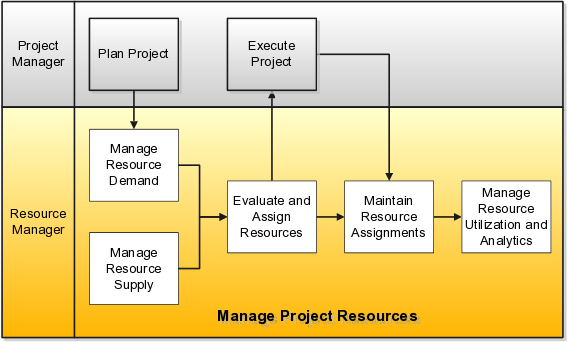
Image Source: docs.oracle.com
Project resource manager uses tools to plan for resource allocation – known as resource planning tools and to assign the resources – known as resource assignment matrix (RAM or RACI).
Refer below figure to understand, how to create a resource plan:
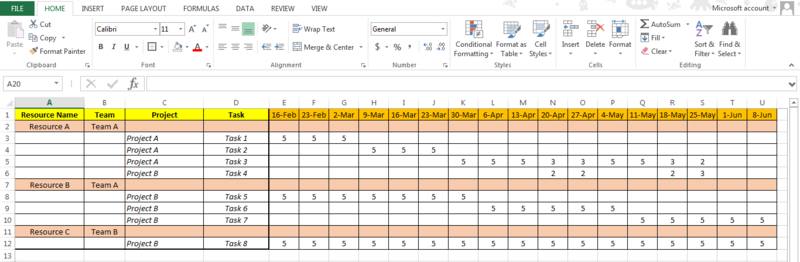
Figure 2: How to create a resource plan
In the above resource plan template, first column identifies different resources as A, B and C.
Second column tells the association of particular resource with related team.
Third column relates resource to different projects followed by specific project tasks in fourth column.
In subsequent column, resource assignment to various tasks for specific hours in a day is maintained. For an example, resource A, in team A is allocated for task 1 of project A on 16- February for 5 hours.
Refer below table 01 to know about resource assignment matrix:
RACI Matrix:
Table 01: Resource assignment matrix or RACI matrix
RACI matrix finds its name from the acronym – R (Responsible), A (Accountable), C (Consulted) and I (Informed).
-
R: defines the person who is assigned to do the work
-
A: defines the person who makes the final decision and has the ultimate ownership
-
C: defines the person who must be consulted before a decision or action is taken
-
I: defines the person who must be informed that a decision or action has been taken
Many organizations have seen project failure even after implementing the best resources management software why?
The reason is, organizations have their processes at different maturity level. And if the resources are not aligned to the process maturity, then it is very likely to meet project failures at initial or later stages.
Many organizations struggle to answer the following set of questions:
-
What are our resources working upon?
-
Are all required resources available for the project with right skills?
-
Are all resources engaged in one or another project?
-
Do we have resources to assign to any urgent project demand?
-
Do we have proper control of assigning resources to different projects?
-
What is the cost variable associated with the resources in a particular month?
-
Can a critical resource be spared for any urgent project needs?
Project Resource management is very helpful to answer above questions and to address the question –
“What is resource management?”.
What makes a good resource?
There are some key principles of resource management. These principles are useful for any organization to manage their resources in projects.
Principles of resource management:
Let’s discuss these key management principles:
1. Resources are usually people:
Project resources are managed with the help of resource assignment matrix such as RACI chart and capacity utilization calculation for different resources. But we can’t ignore the fact that resources are people too, who can’t only be measured by hard data set for their efficiency and effectiveness.
They require some soft skills to manage them efficiently. Skills include communication, leadership, and guidance to be motivated and inspired while working. The data can only tell about resource utilization and resource availability, but cannot increase resource productivity. Hence, a metric can be used to identify the areas of concern. But they can be well addressed by the people themselves. Talk to the relevant resources or team regarding concerns and help them to resolve the same.
2. Key people management:
Involve the resources to achieve common project objectives. Ensure to align all the resources and set expectations. Resources should be clear about, what is expected out of them. They should understand the priority & importance of assigned tasks. They should be involved in project risk identification by encouraging them for open discussion. They should be given the liberty to set and estimate task schedules depending on their priorities. This will increase the resource commitment towards schedules.
3. Principles of team management:
Bring the sense of collaboration among team members. So that all the resources come to the common platform of understanding. This will foster productivity & creativity and eventually decreases the chances of errors. Real time feedback to the team will enhance their confidence and commitment.
4. Principle of allocation:
Always try to allocate the right resources for right tasks. Don’t just assign the tasks to the resources. Always match the resource capability and interest with the task and then do an assignment. Know your resource and his or her interest, Then figure out which task motivates him or her the most. Assign that task only to him or her to keep your resource production.
5. Rewards & recognition:
Also, the efforts of your resources should not go unrewarded. Ensure to make your resources knew about, how important their contribution to assigned tasks was. Recognize their effort and time.
Resource allocation best practices to manage resources effectively:
There are some best practices followed by organizations to allocate their resources efficiently and manage them effectively. Lets discuss them in following heads:
1. Centralized resource pool:
Set up a centralized resource pool for project assignments. Use two important management tools to govern the resource pool – the cost associated with each resource in pool and availability of each resource. Based on these two criteria, manage the allocation of resources to different project tasks.
2. Leveling resource:
Balance the workload of resources, so that no resource is overloaded. Resource leveling needs to be done on a continuous basis to ensure resources are being used effectively and aligned as per the need of task prioritization.
3. Know who is doing what:
Keep the track of resources allocation in real time to know which resource is engaged in whatever activity at a particular moment. This will certainly help to keep all the resources productive and maximize their effective utilization.
4. Track the progress:
One should not neglect the importance of information resource management. Track the progress of ongoing projects in real time to obtain maximum information, to understand the challenges and to anticipate any potential risk. So that there is course correction, if needed and can be executed in advance. Take the help of IT support and IT infrastructure to get real time information pertaining to project status.
5. Future forecasting:
Taking all above points into account, you may come up with future forecasting on resource planning and management. Analyze what went well & what went wrong and accordingly take actions to forecast future demands and capacity planning.
6. Use appropriate RM software:
Some appropriate software can also be used to manage resources effectively. They can provide a user-friendly interface to manage resources in real time. But, my advice is to choose appropriate software for your organization based on the organizational maturity level so that you can utilize these softwares in right perspective.
PMP - Resource Management Model:
Let’s understand, why PMP - Resource Management Model?
After assessing your organizational processes based on program management maturity model for complex large organizations (involved in multiple related projects) or project management maturity models for other organizations, a proper resource management maturity model (RMMM) can be assigned to project phases or activities. This is done to maximize the ROI of resource components.
PMI (Project Management Institute) Resource Management Maturity Model provides a framework. This framework helps to assign adequate resources during the life of the projects based on organizational capabilities for realizing following benefits:
1. Common understanding:
It provides a common understanding among project resource manager, project portfolio manager and business executives. This develops the common language of communicating project deliverables, objectives, issues etc.
2. Self-Assessment:
This framework helps stakeholders & organizations to assess their present and optimal levels of maturity.
3. Decision- making for resources management:
It helps to match the organizational capabilities and maturity with resource management model for projects. Every organization doesn’t require a higher level of resource management maturity.
4. Selection of suitable software:
According to PPM maturity, an organization can select suitable PPM software to manage its resources and to address current and potential needs.
For effective resource management in organizations, there are typically 1 - 5 levels of Resource Management Maturity Model. They are listed below along with an additional level 0 describing “No formal process level”. These RMMM levels are based on PMI defined program or project management maturity models for organizations:
LEVEL 0 – No Formal Process
LEVEL 1 – Work Visibility
LEVEL 2 - Controlled Assignment
LEVEL 3 – Governed Capacity
LEVEL 4 – Schedule Driven Assignment
LEVEL 5 – Granular Management
Now, lets understand these RMMM levels in detail:
LEVEL 0: No Formal Process:
Resources used by managers are allocated on ad hoc basis to the projects at this level. There is no formal process on resource allocation. Hence resources are not effectively utilized under this maturity level and this leads to risky & counterproductive outcomes.
LEVEL 1: Work Visibility:
This level gives organizations an opportunity to know, “which resource is working on what”, But resources are not allocated and assigned to work in controlled way or with oversight.
LEVEL 2: Controlled assignment:
Under this maturity level, there is a formal resource assignment approval process known as “Resource approval workflow or RAW”. However, the resource manager performs approvals by consulting a heat map indicating the availability of each resource and providing approvals only when availability exceeds demand.
LEVEL 3: Governed Capacity:
This level introduces the concept of capacity management. It provides a governance structure, which prioritizes projects over new resource demands.
Under this maturity level, a resource or portfolio governance committee is typically formed. The committee comprises of stakeholders from demand side (Project ideas, proposals, requests etc), supply side (i.e. resources) and business executives. Based on different criteria such as financial impacts, tangible & non-tangible benefits, associated risks etc, project prioritization takes place. If enough resources are not available for all proposed projects, committee can decline to approve some of the projects after project prioritization and approve only prioritized projects to assign scarce resources in the best possible way.
LEVEL 4: Schedule Driven Assignment:
Not all the resources equally participate in all the phases of a project. Thus in this resource maturity level, resource assignment approval and capacity management are triggered by project schedule at phase level. Project resources are assigned according to phase level activity information delineated in the project work breakdown structure.
LEVEL 5: Granular Management:
Under this maturity level, resource assignment approval and capacity management processes are driven by complete and full task level project schedule. This maturity level considers resource assignment at very granular level ie full task levels of work breakdown structure. This level of maturity may be necessary when the phase-level information about resource utilization is too coarse and full project schedule detail is necessary and meaningful to the business.
The appropriate level of RMM Model should be used with related PM maturity of an organization to ensure project success.
Final Takeaways:
In a nutshell, resources indeed are indispensable components of any project and they require to be managed effectively and efficiently. This is done to justify the resource - return on investment for any project. Resources, if not managed well, can result in counterproductive outcomes that leads to project failures. There are some program management principles and practices to follow while managing resources. Also, resource allocation best practices are used to allocate project resources for their best possible outcomes.
The best way is to identify Project portfolio maturity of your organization and take the help of explained Resource Management Maturity model to assign resources properly to different projects in hand. Effective resource management in organizations is a key to successful project orientation.
Ace the project management resource scheduling