8 Common Types of Organizational Structures in Project Management
An organizational structure is a standard hierarchy of operations. It defines how you can divide, coordinate, and direct groups. More so, it defines the positions and describes the tasks required to achieve an organization’s objectives and vision.
Organizational structures aren’t set in stone and are tweaked as per the organization’s size, needs, and their philosophy. In this article, you'll get to learn the nitty-gritty of different types of organizational structures in project management and how they function.
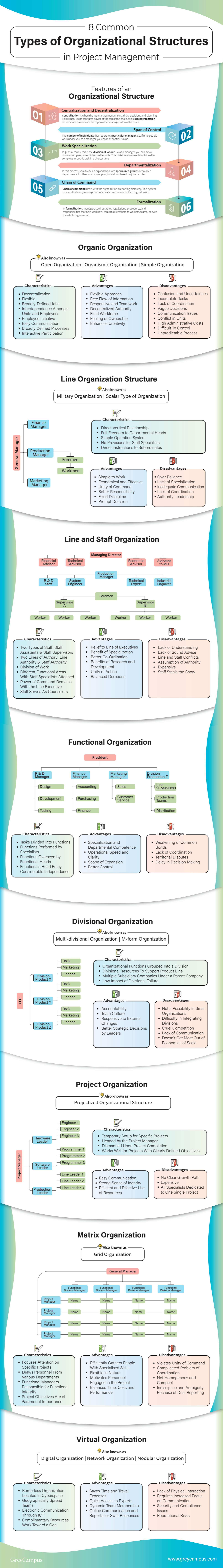
Features and Types of Organizational Structure
When choosing an organizational structure, certain features shouldn't be overlooked.
The key elements that contribute to a proper organizational structure are as follows:
- Degree of alignment with organizational objectives
- Accountability assignment
- Delegation of Capabilities
- Simplicity of Design
- Physical locations
1. Organic or Simple Organization
This type of organization is very flexible and able to adapt well to market changes.
This structure is characterized by having few rules, regulations and management layers and a decentralized decision-making layout.
An organic organization's design deals well with a rapidly changing environment. People work side-by-side to communicate quickly and often solving unforeseen problems, issues and requirements.
Here, the project manager has very little or no authority, and may or may not have a designated job role.
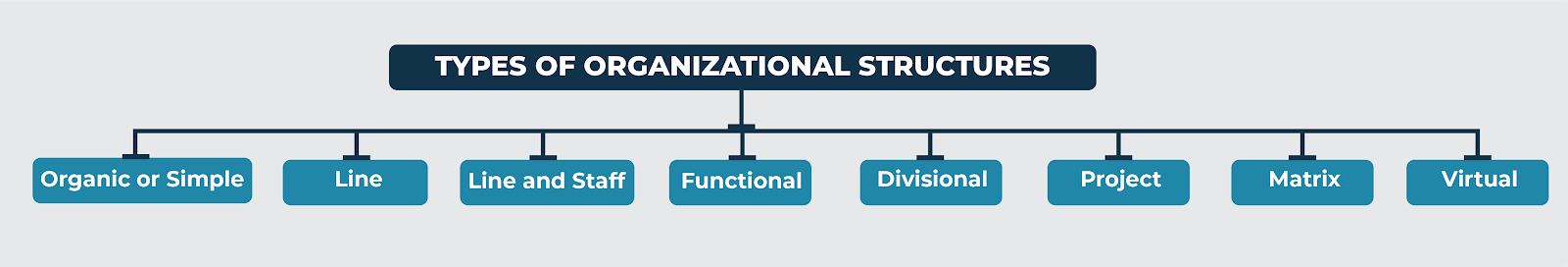
2. Line Organization
This is the simplest form of organizational structure that you'll find across small companies. It has well-defined authority levels in the hierarchical structure. Power flows from the top down to different operational levels or workers.
The hierarchical structure clearly defines authority, responsibility, and accountability at each level.
Due to its simplicity, authority and responsibilities are transparent and easily traceable. Communication is fast and easy because employees get quick feedback and respond fast. Here is a small tech company in Thailand called "Ling"; they have a simple structure. Team members can communicate fast and effectively.
The project manager performs duties based on position or authority in the hierarchy. Some organizations don’t have this position, but when they do, they may have little or nothing to do.
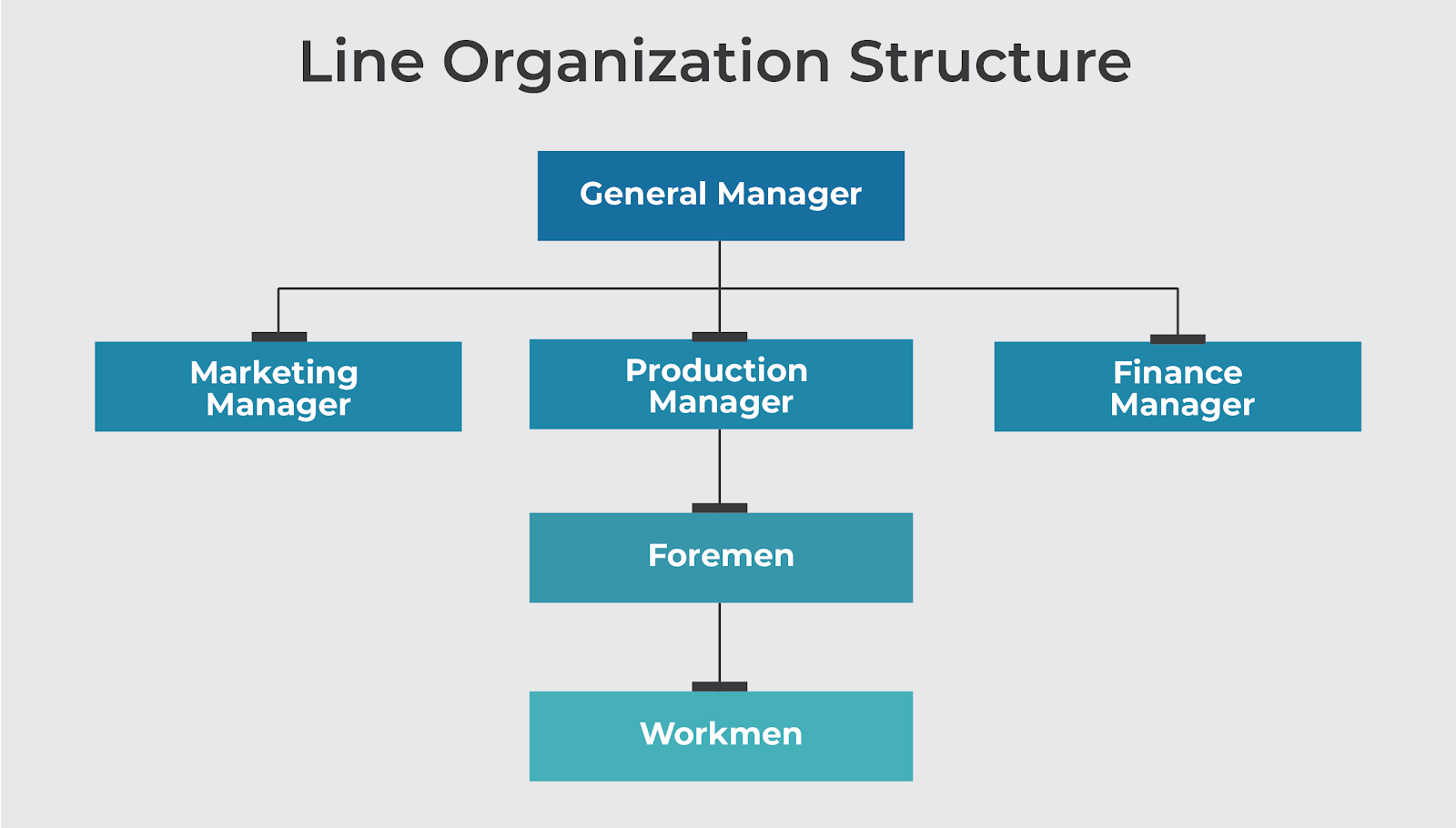
3. Line and Staff Organization
The Line and Staff Organization is a modification of the Line Organization. Here, functional specialists work with line managers to guide and advise them.
This structure is more common in the present day, and most of the larger enterprises adopt this type of setup.
The staff consists of two categories; the general and the specialized team.
- General Staff: The general staff consists of ordinary employees that assist the top management. These staff aren’t experts
- Specialized Staff: This team consists of experts that offer services to the organization. Their roles can be advisory, control (as in quality control), or service (such as maintenance). The Line and Staff Organization uses the expertise of specialists. So the line managers become better in several fields.
.jpg)
Advantages
1) Staff can make quality decisions, get support from specialists, and enjoy better coordination.
2) Get training to enhance skills, get an opportunity to work in research & development.
Disadvantages
1) Increased confusion and conflicts among the staff
2) Higher costs on hiring specialist
3) A tendency to develop personal image within the group
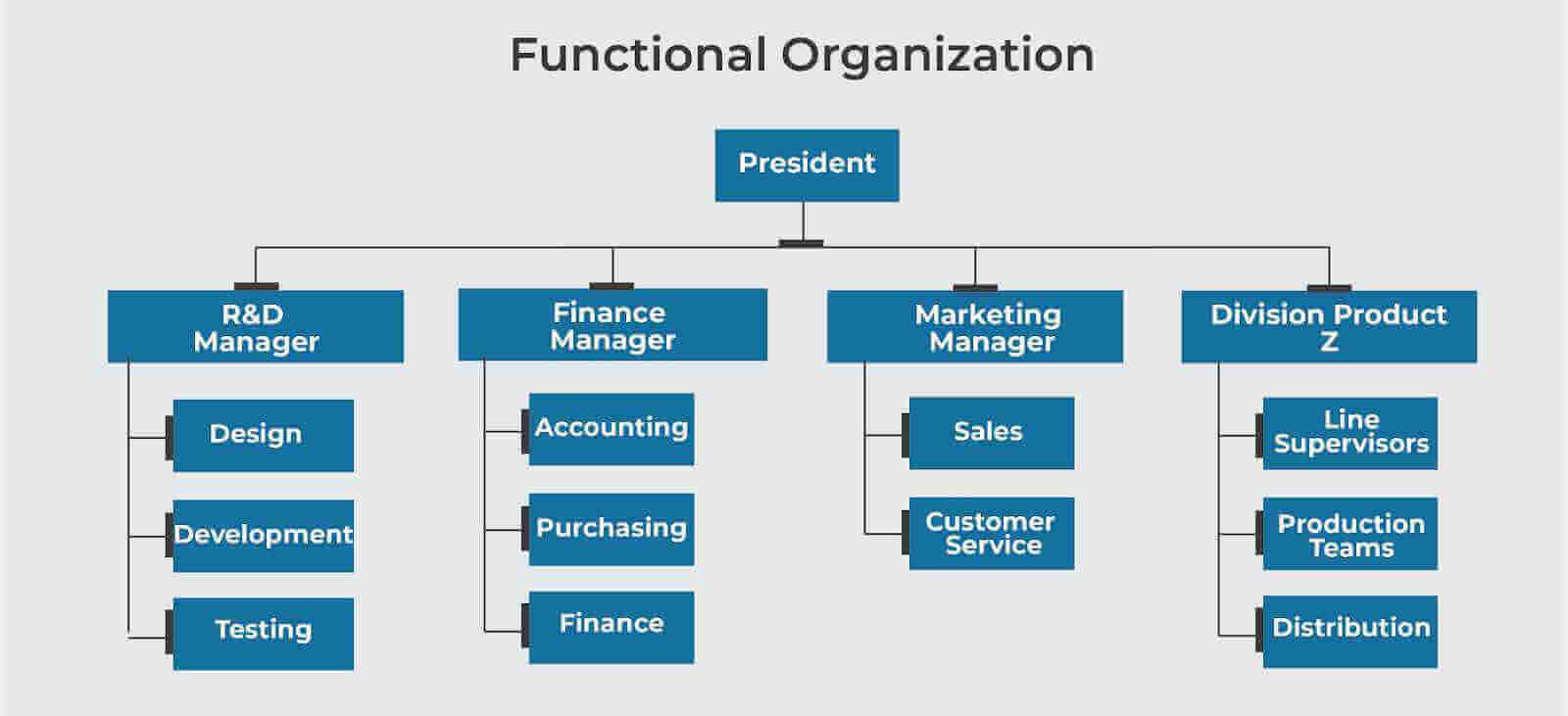
4. Functional Organization
The Functional Organization groups workers based on their area of specialization. This structure is an extension of the Line Organization. The functional manager leads the team and manages all the operations or businesses.
The Functional Organization manager enforces directives within a clearly defined scope of authority. This concept originated with Fredrick W. Taylor.
Here you classify workers according to their functional roles and department. Some of the general departments under this are
- Finance
- HR
- Sales
- Customer service
- Supply Chain, etc.,
The organization's head is the president, followed by the vice president, and the chain goes on. Furthermore, the leaders of departments foresee their departmental performance. So they collectively help the organization control quality and uniformity.
The structure positions departments vertically and disconnected from others. Hence the name “silos.” The department heads manage communication between the top management and his subordinates.
The project manager has a minimal role to play or may not have a designated position. Generally, you'll play the role of an expediter or work as a coordinator. While as a functional manager, you'll deal with
- Budget allocation
- Resource allocation, and
- Decision making
This type of organization is suitable for manufacturing or engineering companies. It supports ongoing operations and practices for product development.
Advantages
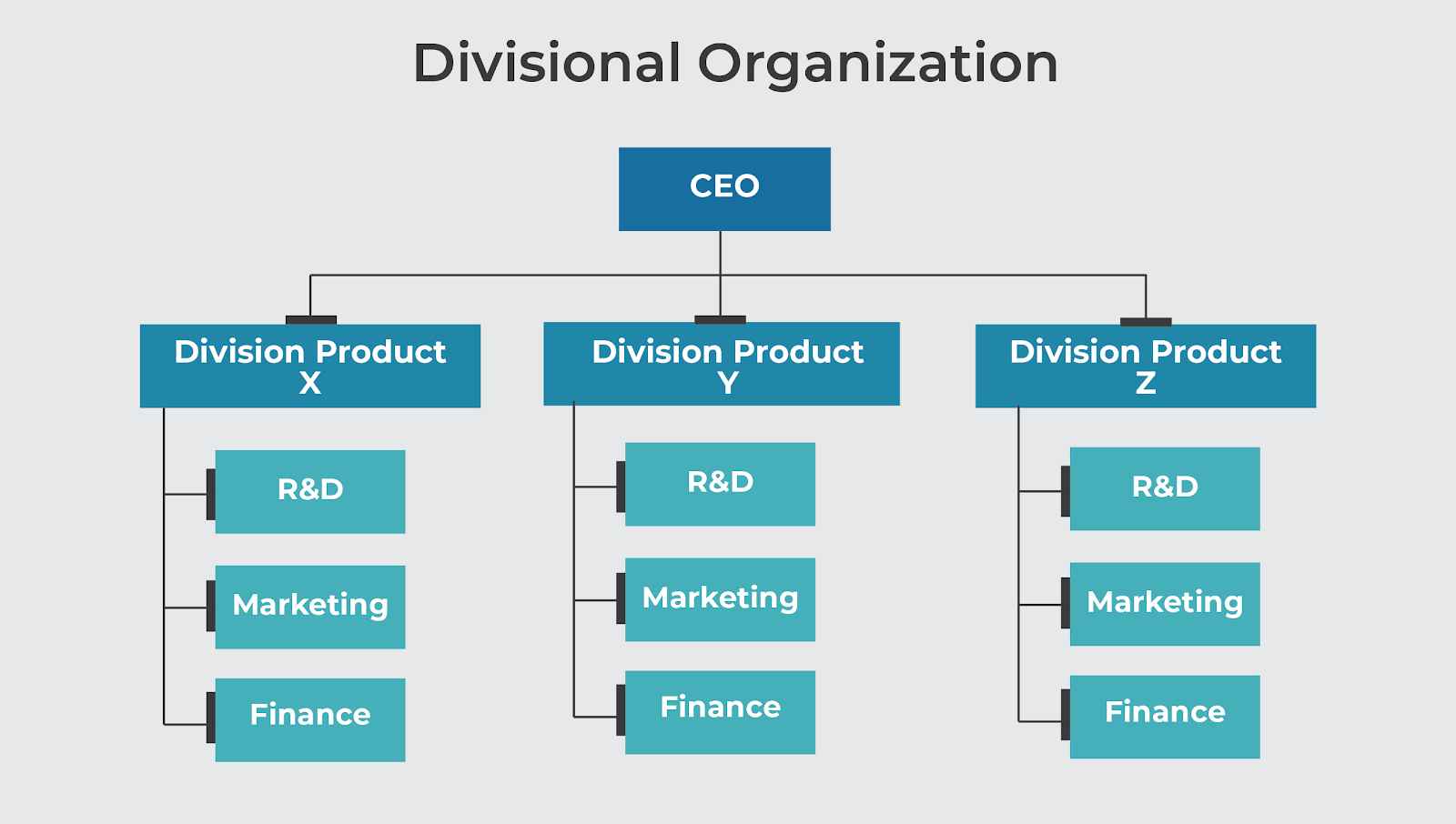
5. Divisional Organization
This type of organization often resembles a Functional Organization. The team members work in different departments. This setup splits the employees into segments based on products, markets, or services.
Albeit, the divisional organization's segments or divisions are autonomous. Functional units that support this structure include:
- Operations,
- Marketing,
- R & D department, and
- Personnel, etc.
This design focuses on service lines like products, customers, area, and time. Since they operate as small organizations, they're called “self-contained structures.”
So they work independently on divisional goals. But all divisions collectively meet the organizational policies and business objectives.
This type of organization is suitable for companies that
- Operate in different geographical locations,
- Have chain stores with subsidiaries, and
- Banking and insurance business
Here, the project managers may or may not exist or may be hired on temporary assignments.
1) This structure affects the integration of the organization as a whole.
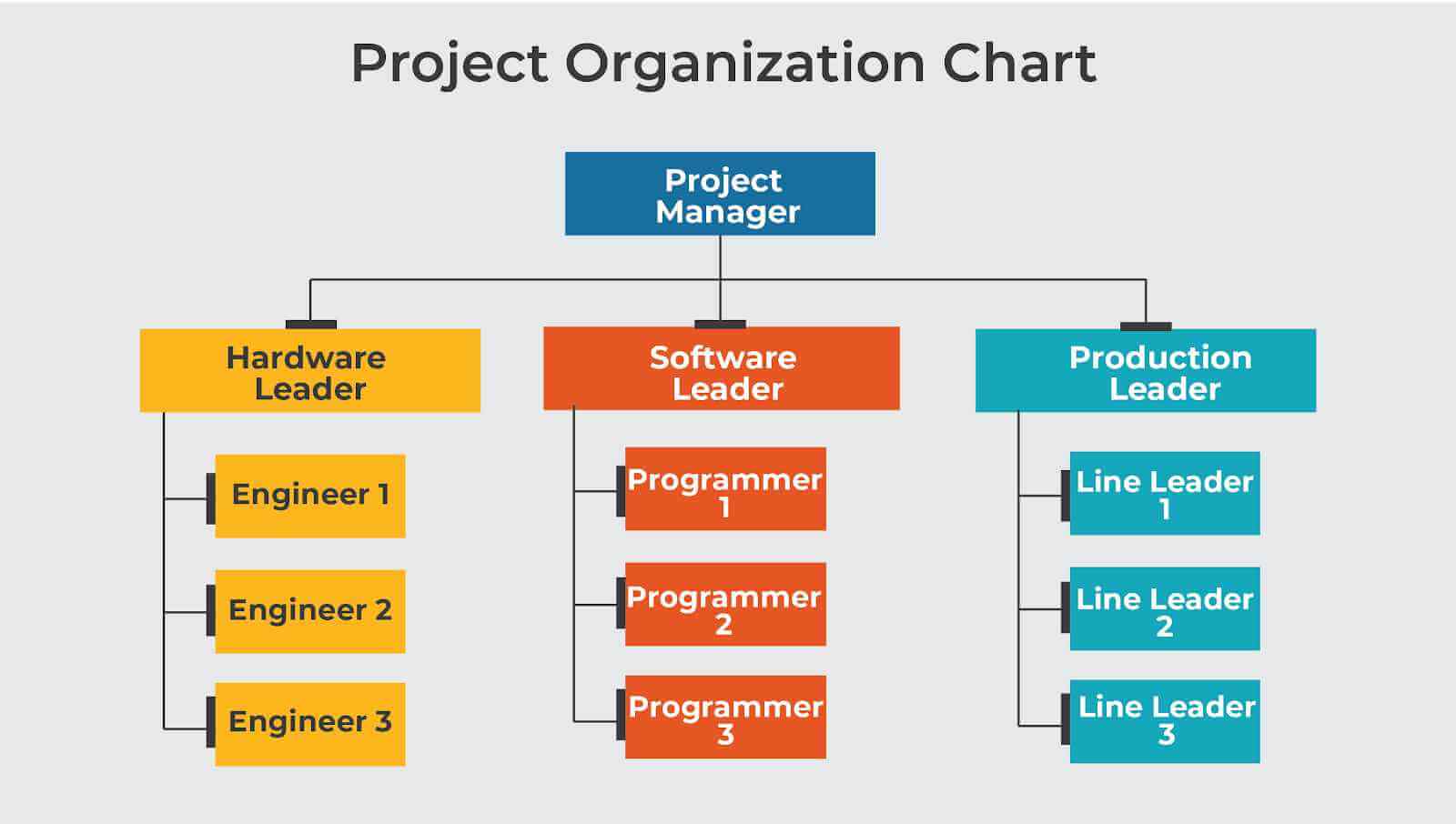
6. Project Organization
Project organization is a temporary setup formed for specific projects. It's also called “projectized organizational structure.” The project manager assigned for the project is the head of this structure.
Once the project is complete, you may choose to dismantle this setup or move it to form a new project. In the case of a new project, the project manager might have to reshuffle the staff to fit the new plan. You’ll hire resources or specialists from different functional departments.
As a project manager, you can use allotted resources until completion and closeout. Albeit you're accountable for all the activities and timely completion of the project. In other words, you must spend based on the project budget.
The manager assigns clearly defined tasks to each of the team members, along with the complete schedule.
These types of organizations are useful when:
- The project scope is complete, and objectives are clearly defined
- The project is unique and independent
Disadvantages
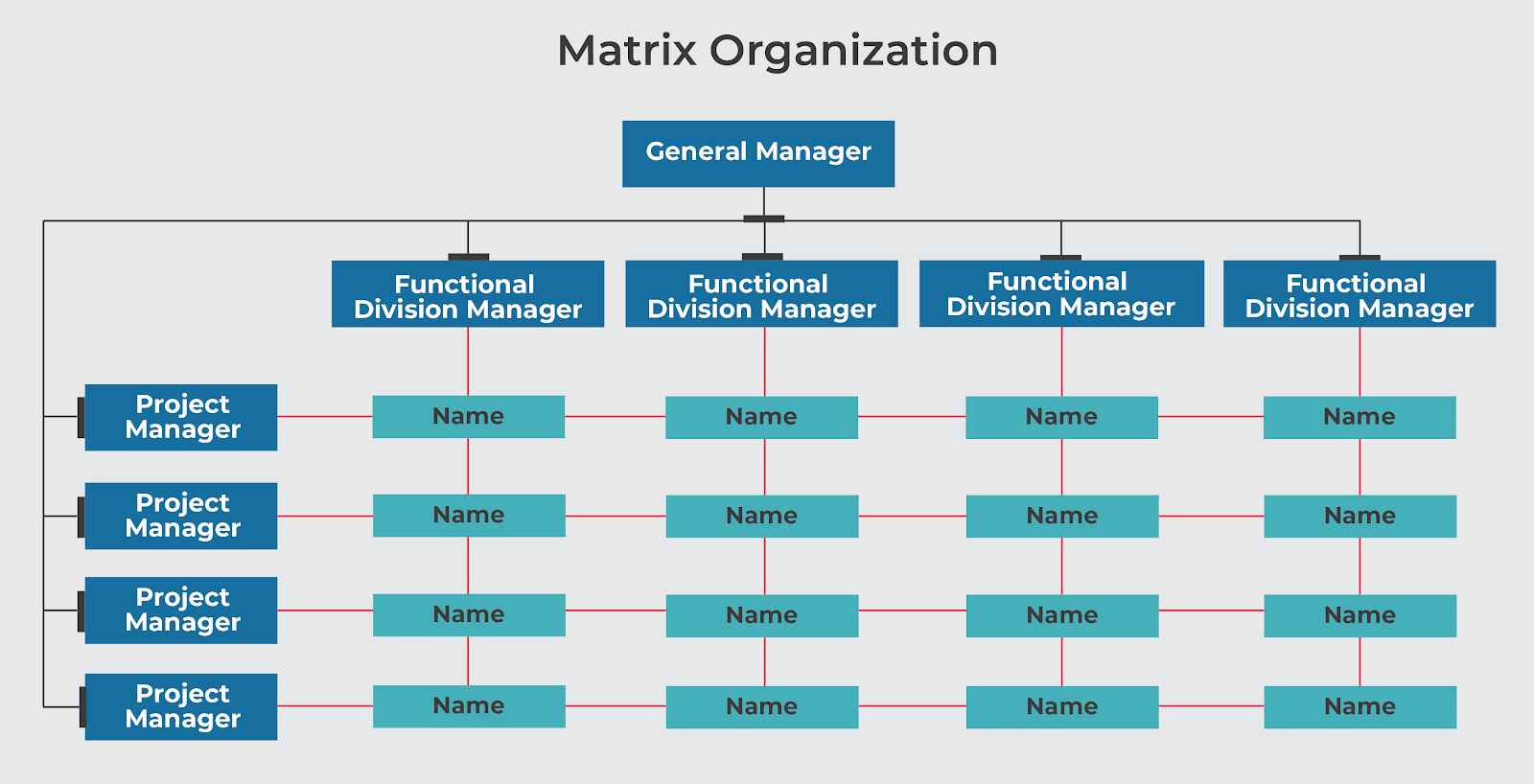
7. Matrix Organization
This one is the combination of a projectized and functional organization. This hybrid organization overcomes the limitations of each organization. Here, both the functional and project managers share their respective authorities.
Project managers are generally responsible for
- Overall integration
- Project planning
- Execution of the project, and
- Completion of project activities
All activities must be done using the assigned resources.
The functional managers are concerned with the operational aspects of the project. They’re also responsible for providing technical guidance.
The functional staff specializes in the skills required for the project. Though project managers manage the project staff, functional managers control the process.
This type of organization is most useful when workers must share available resources. The combination achieves high efficiency and better usage of available resources. Also, they adapt better to the changing trends.
You can further classify the Matrix Organization into
- Balanced
- Strong and
- Weak
The authority level that both functional and project managers share determines its strength.
Disadvantages
8. Virtual Organization
A virtual organization is a recent development that involves different locations. When your team executes a project in one area, you can manage it from any other place. So you can distribute resources to your project team regardless of location.
You can connect all the locations virtually. The other names for this organizational structure are:
- Digital organization
- Network organization, or
- Modular organization
ICT (Information and Communication Technology) is the backbone of virtual organizations. This organization is a social network without vertical and horizontal boundaries.
Resources aren't tied to a particular workstation (desk). Also, you can work from any mobile device. You can manage every project activity, including meetings, virtually.
The team reports digitally except on a few occasions that need physical meetings. Hence, it's common to hear of virtual offices, virtual teams, and virtual leadership
This setup is most suitable for software or IT companies.
Advantages
1) Faster and cost-effective as there are no boundaries to work and communication.
2) Lower operating costs as no permanent set up required (no need for office premises)
3) Have several options like flexitime, part-time work, job-sharing, and home-based working, hence increased
4) Employee satisfaction and efficiency
5) Can have a larger talent pool
Disadvantages
1) No physical contact or communication, thus, lacks team integrity
2) Difficult to restrict information sharing as your locations are different
3) You have to spread resources across various locations and time zones
4) Resources require training for virtual interaction
5) Different time zones cause delayed responses
Wrapping Up
With the different types of organizational structures, it’s easy to know what you need. Though each structure has limitations, large and complex organizations adopt the matrix organization.
Line and staff organization has a direct and straightforward hierarchy. Hence it's used in simple organizations. Software or information technology businesses often adopt virtual organizations.
Albeit choosing the right organization, type ensures that you do well in the market.
Want To Make Ultimate Project Decisions? Sign Up for a Bootcamp Today!