4 ITIL Change Types That You Can Master With a Certification
Not all IT changes are alike, and ITIL is the best way to manage ITIL changes while paying due consideration to their uniqueness.
An indispensable part of modern organizations, the Information Technology Infrastructure Library (ITIL) is considered to be the gold standard of IT service management (ITSM). With four different ITIL change types, ITIL offers IT practitioners with insightful and technology-enabled solutions that are highly valued by organizations across the world.
ITIL is an approach that guides organizations to use IT and digital services as a means to achieve their business objectives and goals. Be it the efficient management of service desk, system administration, or services, ITIL benefits businesses by ensuring growth and facilitating business transformation and change seamlessly. An ITIL certification empowers IT practitioners to learn the change types and implement the framework into their business environments.
Five Phases of ITIL Change Management Lifecycle
Five distinct phases are part of the ITIL change management lifecycle. These phases are ever-present in almost all ITIL change types.
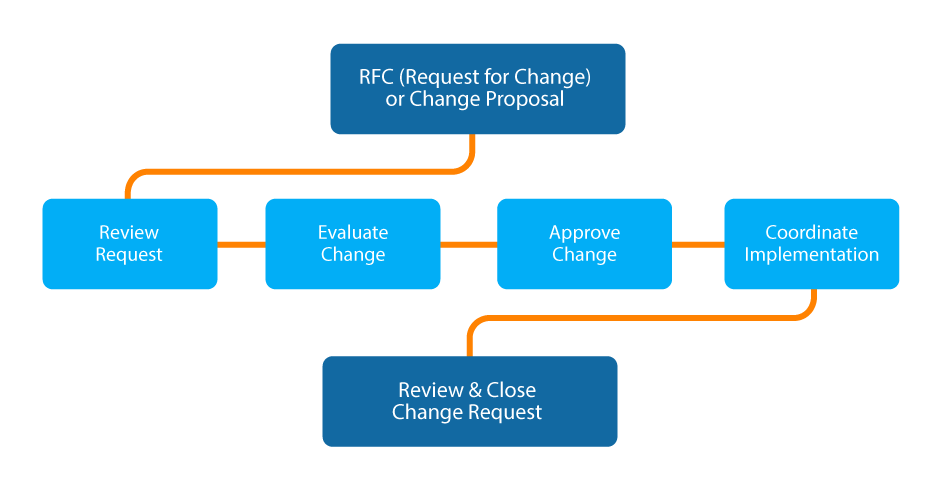
Source: Plutora
- Request for Change (RFC) is the trigger point of a change that is initiated by an individual, generally a process owner, or a business unit. Based on the evaluation of the RFC the authorization and implementation of the change will take place. The RFC will contain the description, type, and timeframe of the change along with the reason and business justification.
- Change Evaluation is carried out and can result in a change evaluation report. It will assess the impact of the change and study how best the change can be implemented without disrupting production continuity.
- Change Approval is provided based on the complexity and type of change. The scope of the change and its risk and impact dictate the approval hierarchy.
- Change Implementation is done by the concerned technical and change management team who will develop, test, and deploy the change. Understandably, this step also involves scheduling the change, its release, addressing training needs, etc.
- A Post-implementation Review concludes the change. This review decides the need for fixes and remediation plans and confirms if the change has been successfully deployed or not.
4 ITIL Change Types You Must Know
Since the inception of ITIL in the 80s, as a set of IT service management best practices and guidelines, ITIL is now seen as a medium through which all IT tasks within an organization are aligned to the business objectives. As a change management mechanism, the types of change ITIL promotes help reduce risks involved in the change. An organization can undergo additions, removal, or upgrade of its processes, software, hardware, manuals, or even the entire IT infrastructures with minimal risk, thanks largely to the use of ITIL change types.
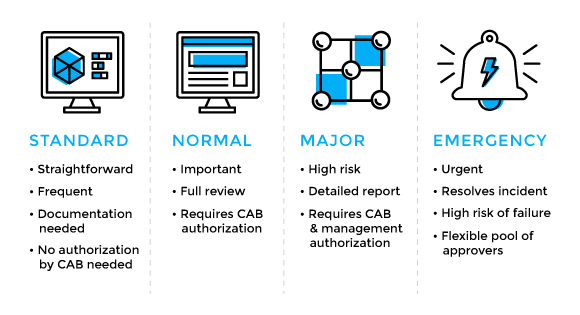
Source: Plutora
There can be different types of change management in ITIL, and there are four specific types when seen through the lens of risk and impact.
- Major Change – A major change is associated with high risk and impact. When not managed efficiently, a major change can disrupt the production and live environment. A major change evaluation will decide on the scheduling of the change, and it will involve a high-level approval workflow. A major change is generally approved by the management and the Change Advisory Board (CAB). Implementation of ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) is an example of a major change.
- Minor Change – Non-trivial changes that rate low on risk and impact are called minor changes. These changes involve all phases of the change management lifecycle, as they don’t occur frequently. This includes the need for a CAB approval. Minor changes are not taken lightly despite their low risk and impact. They are carefully documented from an archival point of view and may be converted into standard changes in the future. Improving the performance of the company intranet portal can be an example of a minor change.
- Standard Change – These changes, like minor changes, are low on risk and impact. However, these are periodic changes with set standard operating procedures built around them. Therefore, these changes are already approved and defined. Due to their regular nature, standard changes don’t follow the usual change management lifecycle and don’t require CAB approval on each occurrence. Deployment of a new patch in one software in an organization is an example of a standard change.
- Emergency Change – Among all ITIL change types, an emergency change is an unexpected interruption that calls for a speedy resolution. There may be necessary changes in the change lifecycle to accommodate this quick change. A security breach of an organization’s IT network would need an emergency change.
Use Cases for ITIL Change Types
Major Change Use Case – ERP Implementation
Changing or implementing an Enterprise Resource Planning solution would amount to a major change in IT. An ERP implementation scenario project scope defines rollout strategy and implementation timeline. A readiness assessment is done for the workforce and the organization and stakeholders are identified. The project milestones, critical success factors, and deliverables are decided with the stakeholders and the post-implementation transition process is forecasted. With the successful ERP implementation, the major change is complete, and exercises like job redefining and competency needs are assessed.
Minor Change Use Case – Performance Improvement
Improving the performance of an in-house portal or workflow management system would be a minor change. While it will require stakeholder onboarding and communications, these changes don’t pose a major risk to the production continuity or service delivery. The RFC will, nevertheless, incorporate the description of the change request, the business justification, and the suggested implementation timeline.
Source: Zero Outage
Standard Change Use Case – Patch Implementation
Implementation of a patch would involve the preparation of an inventory of the components in the IT infrastructure, risk and sensitivity rating of the infrastructure for prioritizing patch implementation, development of test environment, patch testing, deployment, and maintenance. The standard change description is accompanied by an implementation timeline and plan, the development of the testing environment and testing plan, and a back-out plan.
Emergency Change Use Case – IT System Security Breach
In such a case, the RFC may have to be assessed along with or after the implementation. Similarly, an emergency CAB may have to evaluate the change and expedite the approvals. Given the fast nature, the post-implementation review of an emergency change is extremely critical. It will not only confirm the successful implementation but also assure how such breaches can be avoided in the future. The detailed post-implementation documentation of the emergency change is mandatory as a part of ITIL best practices. An emergency change plan may factor in the communication plan, test plans, back-ups and their subsequent restoration, and review of the test plan including provisions for performing test transactions.
Benefits of ITIL Change Management
With its different change management types, ITIL brings in a bouquet of benefits for ITSM. The use of ITIL not only manages the risk and impact of the change but also ensures the continuity of the Business As Usual (BAU). It can effectively eliminate unauthorized changes while ensuring the optimal use of resources. ITIL ensures better communication flow and clarity in authorizations and approvals.
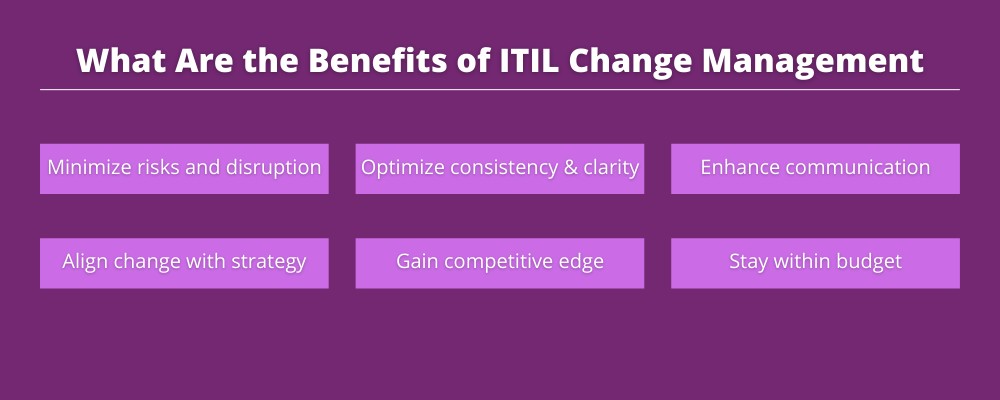
- Risk and Impact Management – Based on the ITIL change request types the organization can assess the risk and impact of the change. Using the ITIL framework helps the IT practitioner handle the change while giving due consideration to the risks involved. This ensures that no risk is underestimated and the impacts are adequately cushioned.
- Continuity of BAU – ITIL change management is beneficial in safeguarding the continuity of live environments. Flawed implementation of a small software patch can disrupt the flow of a process, which in turn can affect the service delivery. ITIL makes sure that there is a robust test plan to check the accuracy of the change before their eventual deployment.
- Ensuring Proper Authorization – ITIL framework requires adherence to a strict change management approval hierarchy. This ensures that changes are implemented in a controlled and manageable environment. The authorization also ensures that the change request and the change itself are properly evaluated and the concerned teams are ready to successfully develop and implement it.
- Effective Use of Resources – Stakeholders and approvers are identified, as are the responsibilities of the resources involved. ITIL fosters control over the change management environment, with clearly communicated roles and responsibilities. This optimizes the utilization of resources in the change process.
- Customer Satisfaction – Erratic change management wouldn’t go unnoticed in the eye of the customer. It will impact the service that you provide, which will eventually lead to customer dissatisfaction. ITIL change management will not only bring in better handling and fewer disruptions, but customers will also be aware of downtimes and service unavailability if any.
How to Master ITIL Change Types with a Certification?
With ITIL, an organization can ensure that its service delivery is consistent and predictable. A certification in ITIL qualifies you in the framework and enables you to add value to the ITSM (information technology service management) functionalities of your workplace. It also helps you manage your change management responsibilities better as you have better insights into the framework. With certification, you are aware of the bigger picture, wherein the importance of IT services and infrastructure in business becomes clearer.
An important part of the ITIL Foundation certification is service transition. It addresses change management in ITSM with an emphasis on risk management and smooth transitions. Services, or parts thereof, need changes from time to time. The replacement may also be required to address obsolescence. A certification will help you follow the ITIL change management and risk management protocols more effectively.
Besides, an ITIL-certified professional will be able to better plan and manage resources and skillsets. You will make better use of tools, software, and personnel in the development, testing, and deployment of change.
Being ITIL certified, you will evaluate a newly developed change, assess the impact of the transition, and the service capability before the release or deployment of the change. With the certified understanding of ITIL, you are better equipped to reduce failure of changes and their impact on the operations.
With ITIL certification, you can integrate interrelated service assets. A change in one part of a process can have an impact on another process, due to interdependencies. As an ITIL-certified change manager, you will be better at ensuring successful implementation of changes and transitions in all related service assets, without affecting the stakeholders and customers.
A certified ITIL professional will not be looking at change management in isolation. A change can interface with other ITIL service management processes, and certification prepares you to manage this interface better. Such processes include problem management, configuration and asset management, release and deployment management, IT service continuity management, security management, knowledge management, request fulfilment, and portfolio management.
The GreyCampus ITIL 4 Foundation Course is a comprehensive training module that equips IT professionals with an understanding of the seven principles and fundamentals of ITIL, four dimensions of service management, and service value chain. It is an AXELOS accredited course that suits the skill requirement of IT professionals who are planning to work in ITIL change management functionalities.
To Sum Up
With GreyCampus ITIL 4 Foundation training and certification you will be a vital asset in your organization’s ITSM processes. As a part of ITIL change management, you will be a part of successful change implementations and help in the reduction of service disruptions. You will be able to lower incidents related to changes, improve the change implementation timelines, and ensure improvement in service marketability. Change, as they say, is the only constant and a certified mastery over the various ITIL change types makes you the ideal resource in your organization to lead and manage changes.