ITIL 4: Six key benefits of the latest version
ITIL is a vital support pillar of any modern IT organization today. ITIL aligns to IT business strategy and deliverables. ITIL framework updates:
ITIL v3: Launched in 2011.
ITIL 4: Launched in the first quarter of 2019 for Industrial revolution 4.
ITIL version 3 is involved in tackling organization challenges. It is based on IT processes for an organization as well as individuals right from the foundation, practitioner to expert level.
ITIL version 4 is an updated framework. It has been updated keeping in view the new era technologies and the vision of IT firms.
With the release of ITIL 4 Foundation, let’s take a look at some of the most prominent benefits that this new framework has to offer!
1. Flexible practices:
ITIL v3 processes have moved to practices in ITIL 4. Practices are an updated version of Processes in ITIL v3. Practices are more practical and simpler that makes them flexible as well. It results in a holistic approach for organizations. The previous process-oriented approach is a major change in ITIL 4 that helps organizations to adopt a more flexible environment. These are a set of organizational resources that helps in performing work or executing and objective.
ITIL 4 has 34 practices covered under:
-
General management (Supplier, Project, Knowledge management etc.)
-
Service management (Incident, problem, change management etc.)
-
Technical management (Deployment, infrastructure management etc.)
2. Holistic approach:
A holistic approach to service management is key in ITIL 4. The holistic approach is defined under four dimensions that add value to customers and stakeholders.
The four dimensions include:
1. Organizations and people: An organization needs a culture that supports its objectives, and the right level of capacity and competence among its workforce. Each organization hierarchy follows a vertical or horizontal structure. The hierarchy comprised of skilled workforces at all levels. Each level in the hierarchy has its own competency as well as roles and responsibilities. Leadership in the organizational setup take care of the workforce to deliver.
2. Information and technology: Technology is to IT service and IT service management. It ensures that business functions properly for the management of IT services. Information management plays a role in customer value and monitors future demands.
3. Partners and suppliers: Partners and suppliers are external to the organization and its workforce. Service relationship and strategy between partner and organization is a two-way communication as they have the same goals. Relationship with the Supplier is not a two-way communication organization can move to other suppliers easily as per its preference and contract. Both are critical to service integration and delivery.
4. Value streams and processes: Value streams help in the creation and delivery of products and services for customers. It aims for minimum waste and maximum value right from input to output processes.
3. Adapts and aligns as per new era technologies:
ITIL 4 approach covers the technologies under Industrial revolution 4. Robotics, AI, nanotechnology, IoT, automation, quantum computing, biotechnology, etc. Due to digitization, the complexity has increased and ITIL 4 will able to help organizations to adapt to it. It has a future proof approach for business as it addresses the digital approach.
4. Focus on practices for organization as well as individual level:
ITIL 4 has seven guiding principles that are useful for IT professionals to adopt that ITIL guidance to their own specific organization environment.
The ITIL 4 guiding principles are recommended for an organization as they can help them to adapt to the changing approach to IT services by using ITIL as the base.
1. Focus on value: Helps to know how customers are using the services, focus on staff value, improves initiative, and customer experience.
2. Start where you are: Work with the available resources and reuse the available one. Improve were ever is the scope.
3. Progress iteratively with feedback: Going to agile method finding out how the customer rates the end product and how we can add value as a service provider.
4. Collaborate and promote visibility: Transparency is important at each level. Working together, building trust results in better outcomes.
5. Think and work holistically: Adopting end to end approach as per 4 dimensions of ITIL 4.
6. Keep it simple and practical: Backtrack from the output and check the steps involved are minimum and simple.
7. Optimize and automate: Follow automation to automate frequent tasks and make them effective.
ITIL 4 focuses on automation, collaboration and keeping things simple. These reflect principles found in Lean, Agile, and DevOps methodologies so should be followed at every stage of service delivery.
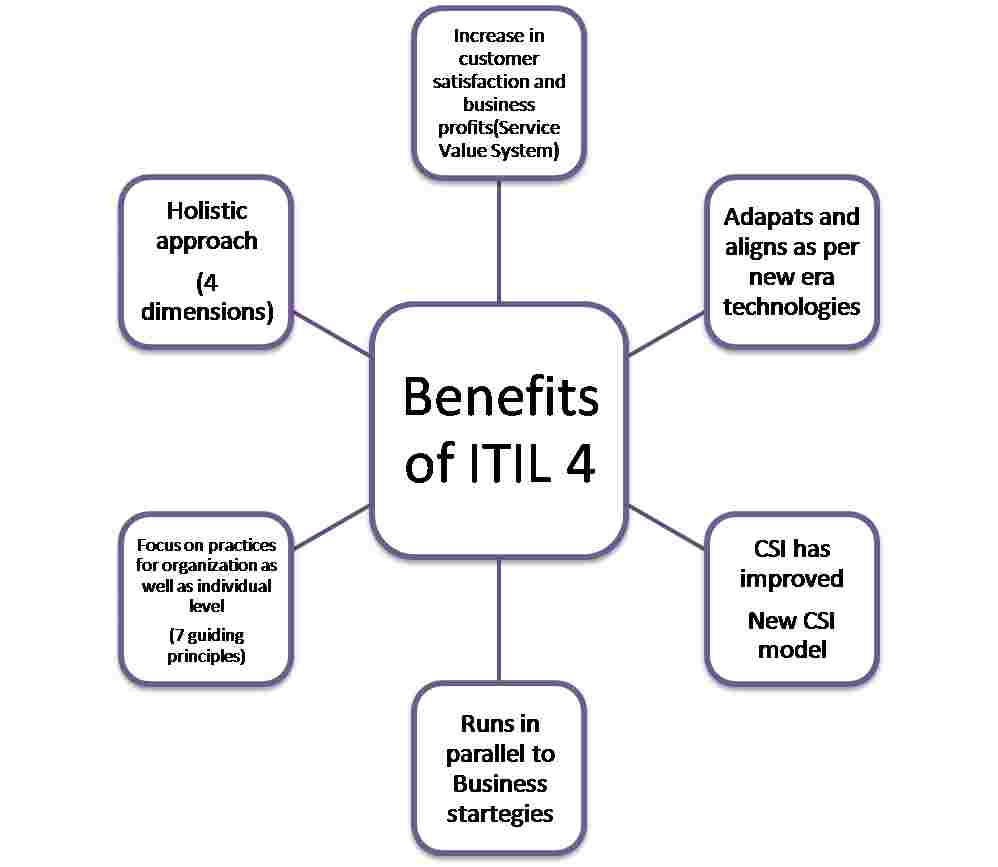
5. Increase in customer satisfaction and business profits:
he service value system (SVS) focuses on business strategy that results in a mutually valued outcome. In this system, all the components and activities of an organization work together to enable value creation. As the SVS has interfaces it creates an ecosystem that helps to create value for organizations, their customers and stakeholders.
Let us look at how SVS supports value chain under six activities:
Source: AXELOS, “ITIL Foundation: ITIL 4 Edition” (2019)
Engage: It involves the engagement of suppliers or partners for service delivery.
Plan: Planning and estimating on the availability and requirement of future resources.
Improve: Improve where ever necessary as there is always a scope of enhancement on the existing user experience.
Design and transition: To decide how the product or services are to be built that are fit for purpose and fit for use. How they are going to be delivered in the market. While designing we have to keep in mind the service performance information.
Obtain build: Makes sure service components are available as and when we need them. Input for this step would be architectures or policies for the organization, engagement of suppliers and partners and requirements we will get from last that is a step of design and transition. All these activities are interrelated.
Deliver and support: This activity ensures that services are delivered as per customer demands and expectations. (similar to service operations in ITIL 3)This ensures seamless delivery of products and services.
All these activities included in SVS have interactions between them which help to have continuous feedback all through the chain. There are 34 ITIL 4 practices that are used in SVC activities. The flexibility of the service value chain allows an organization to be efficient when it comes to changing stakeholder requirements and expectations.
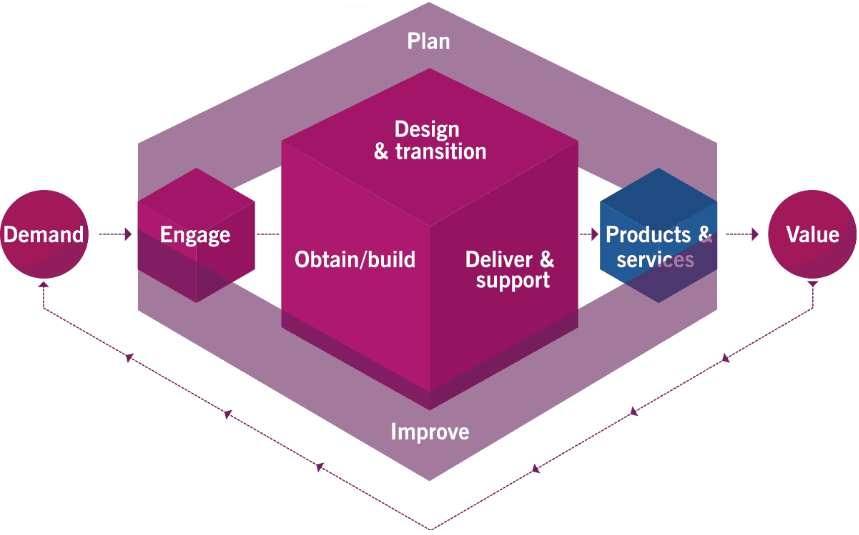
6. CSI has improved:
The lowest block in service value system is Continual Service Improvement. CSI basically recalls the practices to be undertaken with changing the need for managing products and services. CSI model has improved in ITIL 4, which the vision that ongoing practice never reached perfection, so there is always scope for improvement. As the name says, the process of improvement never stops it is continual.
The top leadership is involved in vision creation. The seven guiding principles are involved all through the below steps involved in the CSI model. It based on Agile, DevOps, and lean methodologies.
Decide on the vision
Define the vision of the initiative. Future of organization and its objectives.
What is the current state?
Current state assessment using reports. What is the quality of services we are delivering now, and what are the steps involved to deliver that?
Where do we want to be?
It involves assessing and analysis how we are going to reach our vision. KPIs and CSFs help to figure out goals by setting business based targets.
How to Plan out till the goal?
Detailed plan to reach the goals set in the last step. The requirement is to check progress throughout the plan.
Take action
Follows agile methods that are delivering in small iterations. Measuring the progress, risk management, and visibility is to be maintained until the delivery.
Did we get there?
Comparison from step 2 to what is achieved at the end of step 5. Analyzing the delivery of services to targets.
How do we keep the progress going?
Keep up with the positive progress going on. From here, we move again to step 1, and the CSI model will go in a cycle manner as we always continue to aim for improvement from where we are.
From the above benefits of ITIL 4, we can have a clear difference it has bought into IT service management with a forward approach to change IT technology at present and in the pipeline. So far, we have seen the ITIL 4 has benefits that simplify the work of ITIL Practitioner as well as the organization. Besides this ITIL 4 certification path is more streamlined for ITIL journey of Practitioners while ITIL V3 certificates still remain valid.
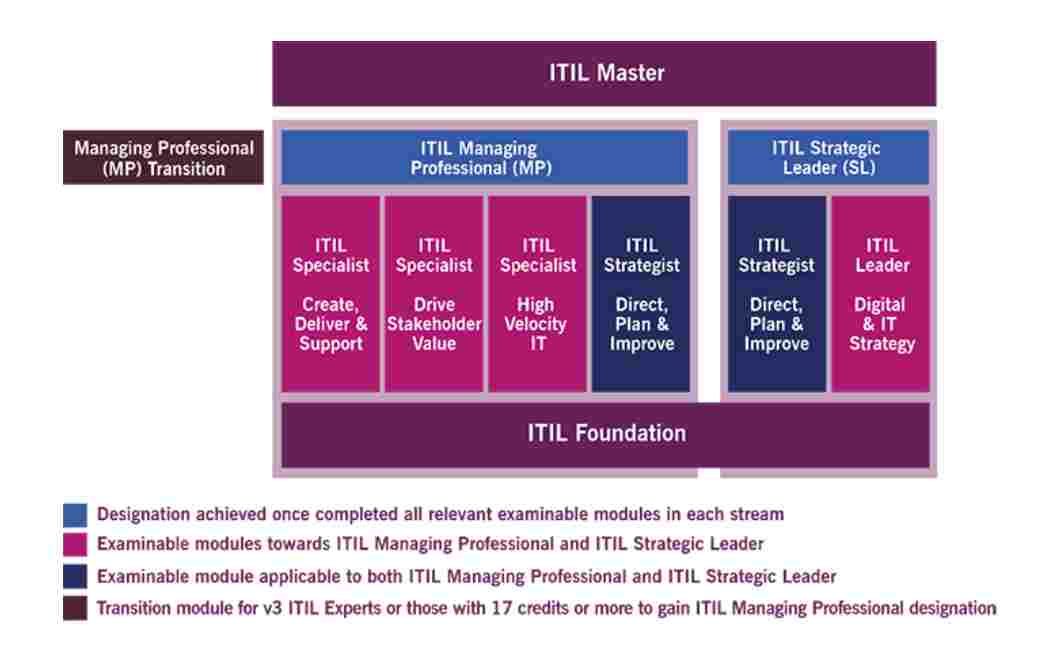
Source: AXELOS, “ITIL Foundation: ITIL 4 Edition” (2019)
The above representation shows from Axelos shows modules involved from Foundation till Master level depending upon the target of practitioners. So, the practitioner can either start from ITIL 4 foundation or reach ITIL expert and then take MP transition certification. The various milestones will be:
-
ITIL specialist
-
ITIL strategist
-
ITIL leader
ITIL 4 doesn’t completely rewrite the ITIL v3 as you go along you will see the core elements are same only things have moved from process lead delivery approach to value-driven systems. ITIL 4 additions are for new emerging trends in software development and IT operations. It takes into accounts new ways of working in DevOps, agile, and lean as well. It not only benefits the ITSM professionals but all those who are delivering and working for digital services.
What next? Get ITIL 4 certified!