Phishing E-mails: Successful Tips to identify and respond to such attacks
Introduction
Phishing is a type of social engineering attack that seeks to exploit the human link for information. When these kinds of fraudulent acts are performed using emails, it is called phishing. The use of the phone to spoof someone and get the information is called Vishing or voice phishing. The use of SMS for the activity accounts for Smishing or SMS phishing.
In this article, we will be discussing- what phishing is, types of phishing, risks associated, identification and response techniques and common scams that got highlighted.
Phishing attacks have become so common these days that almost all big companies hire cybersecurity experts to perform mock phishing exercises so that the employees are aware of the scenarios and risks associated (also consider checking this perfect guide for cybersecurity certifications). The simulation can be done in-house or can be vendor driven. There are a couple of companies that specialize in conducting phishing simulations. Check this out: https://www.knowbe4.com/phishing-security-test-offer. The knowledge of phishing is not only for those who work in information security but for the common man as well. The target is both organizations as well as the society.
What is a phishing email?
Phishing is an act of sending emails to individuals and organizations in order to trick the victim into revealing sensitive information. The emails are crafted in such a way that they look like legitimate emails. Still, there are some traces that the user can see and distinguish a phishing email from a legitimate email. Below are a few common types of phishing, apart from the general phishing.
- Spear Phishing:
Phishing emails are generally broadcasted so as to increase the chances of success. In spear phishing, the target is a particular individual. The emails will be crafted keeping the situation of the person in mind. The email will be personalized so that the user gets tricked. - Whaling:
The art of tricking the “bigger fish” in the market. The targets are usually high profile people who are in powerful positions. They can be the CEO of an organization, or politicians, businessmen, etc. The content will be crafted in a way that will masquerade a business issue or something that is critical to the company and requires immediate attention.
What are the risks?
What could possibly happen when a phishing email is opened? What if the attachment is opened? What if the links in the email are clicked? Let’s find the answers to these questions. Below are common risks associated with phishing emails.
- Loss of Confidential data
Phishing emails try to seek information from the users. Providing this information may seem harmless at first but this can be used to launch secondary attacks (Here's a resource that will navigate you through cyber security attacks). The information asked, can be a series of questions: Email ID, Mother’s maiden name, what was the name of your first school? aadhaar card number/social security number, etc. This type of information may be used to compromise other accounts. - Credential compromise
Phishing emails usually have pdf attachments which are password protected. The emails will have the directions to what the password is; e.g. “The password of the invoice is same as your bank account password”.
The user may be prompted to provide the username and password to unlock the attachment. This will send the credentials to the attacker. This can be checked using a traffic analyzer. We can analyze the traffic packet with Wireshark and see the credentials traveling back. - Network mayhem
The attachment or links in the email can be malicious. They can spread through the network very fast, almost as soon as the file is clicked. The malware will block the bandwidth of the intranet and may try to download further malware from the internet. - Monetary loss
Phishing emails may try to trick the users into providing credit card details, bank details, etc. Once the users enter the information, it is used by the attacker to perform unauthenticated purchases.
Latest phishing email attempts (Examples/Samples)
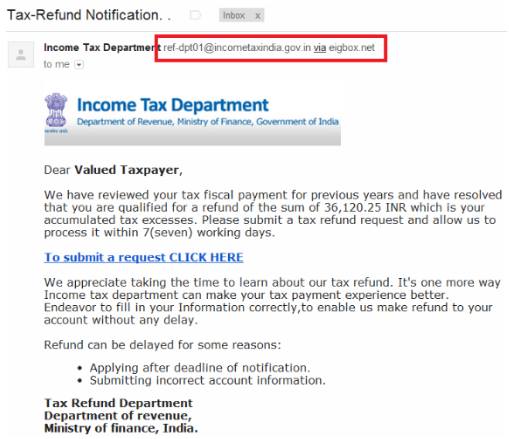
- Income tax
Emails that seem to come from income tax department mentioning that a refund has been initiated, and asking you to click on the link mentioned to log in to your account. For ease of access, the user just clicks on the mentioned link and tries to login with the credentials. The link is spoofed and the customer loses the credentials.
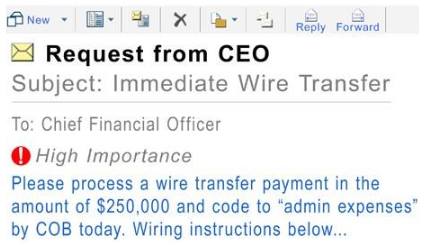
- CEO fraud
The fraudsters will send emails to the finance department requesting money transfers. The recipient if tricked will transfer the money without further inquiry as it seems that it has come from the CEO. The attackers are smart enough to add a clause that they are busy and hence other information will be provided later (if any).
Anatomy of a phishing email
- Suspicious headers
Since the email is spoofed, the sender name would be different. Are you really expecting a mail from such a sender? Check for the sender address carefully before you respond. - Nonuser-centric
The phishing emails are broadcasted and hence are non-personalised. The emails will be addressing the users as “Dear Customer”. Any legitimate emails will address the users by their name unless the content of the email is generic and is valid for all the users like ads, promotional offers, etc. - Spelling errors
Check for spelling errors. The emails may have spelling mistakes, like the word “Amazon” may be spelled like “Amazan”. - Poor grammar
The grammar of the emails is generally bad. Depending on the origin of the email, the style of writing differs and hence this gets reflected in the email body. The email might have been written in a different language, and then converted to English. - Formatting issues
The emails are spoofed and sent using non-standard clients. This may cause compatibility issues which can change the formatting of the email. The body may have been left or right aligned. The links and photos might be out of order. You may see embedded frames or codes. - Suspicious links
Most phishing emails will have hyperlinks and URL mentioned in the body. These are crafted in such a way that the destination is either malicious or will be a spoofed website. Users should refrain from clicking on any such URL. If required, it is better to search the website and log in manually. - Suspicious attachments
Attachments are another component of a phishing email. The attachments can be invoice, instructions, statements and zip files. These are used to steal the credentials of the users as they are password protected. Another possibility is that the attachment is an excel file with a macro virus embedded. - Sense of urgency
Phishing emails will try to create a sense of urgency. This is done so that the users take action on a whim and regret later. Sentences like:
- “If you do not submit, your account will be deactivated”
- “Urgent action required– last day”
These are examples of sentences used by fraudsters. This leaves users with little time to think. - Having all the Ace’s
Does the email seem to be too good to be true? Have you received an email from a subscriber offering unbelievable deals? Do you not sense something fishy here? Else, how will the user be tricked?
How to respond to a phishing email?
- Report spam
All email clients have an option to report spam. This will block the sender from sending emails to you. The emails will actually be placed in a spam folder and can be accessed by opening it. This approach takes time as the senders will keep changing the addresses so that the emails do not end up in the spam folder. Still, it is recommended that the emails be blocked just in case the sender remains same. - Do not respond
Do not respond to that email as there will be no one to read that email and respond. The situation might worsen and you may start receiving more spam emails. - Delete the email
Delete the email right away. This will avoid accidental opening and click on the links/attachments later. Who wants to keep a malicious email in their inbox anyway? Delete it permanently. - Do not spam the spam
Do not forward phishing emails to others. If you are in the connected network and you forward the email, the chances that the email will be opened will rise and same for the network infection.
Other types of Phishing Scams
- Nigerian scam
One of the oldest kind of scams that originated from Nigeria. A distant person will offer you a huge sum of money to either invest in some business or inherit it. The scenario is created in a way that seems illogical today but some big shots have been on the hook through these emails.

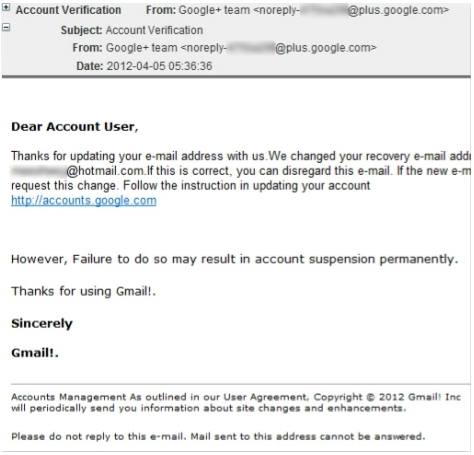
- Account deactivation scams
The user will receive an email that the account needs to be activated using the below link. The emails will also create a sense of urgency; e.g. failure to activate will result in PERMANENT account deactivation.
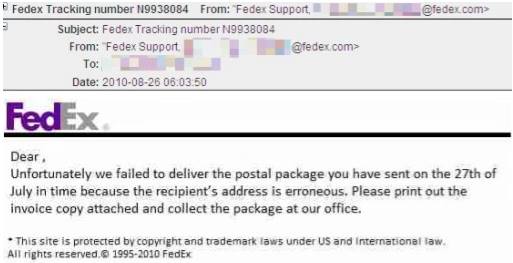
- FedEx parcel tracking – Invoice
A very simple and legit looking email regarding your FedEx parcel, if you are expecting one. The email will create a scenario that requires you to open the attachment and get infected.
In a nutshell
Now you are aware of what phishing is and how Phishing emails can be detected and responded to. Where to look for the signals and how not to fall prey to the common scams. You can put your knowledge to test in the real world now. For starters, you can take a simple test to identify if the emails are phishing attempts or legitimate. Before you start, let’s recap a few points:
- Unknown senders
- Mismatched URLs
- No use of spell checkers
- Asking for money? Don’t give
- Giving away money? Don’t take it
- Asking for help? You seek help with the email.
Test link - https://www.sonicwall.com/en-us/phishing-iq-test
One bit that has remained untouched in this is the use of technology as a preventive measure for phishing. The use of a good email filtering solution is what is required. The solution will decide what is to be delivered and what not.
Email filtering rules:
- Mail headers. Legitimate senders have unique message IDs. They usually use traditional software to send emails. These are listed in the header. Spammers may try to imitate these, but they eventually end up using the same header again.
- Subject and message content: Keyword filtering scans for image-only messages or unconventional colors/fonts.
- Sender: Block known bad senders and ISPs.
Attackers are dynamic and so should our filter be. Some of the most prominent enterprise email filters are SPAMfighter Pro, FireEye, and SpamAssassin. Still, there are cases of compromise due to phishing. The device will do the job as directed by the rules but for a really smart phishing email, you need to keep your eyes peeled. Stay alert, Stay safe!
Want to learn more about Ethical Hacking? Enroll now!
