Top 7 Cybersecurity Threats You Can Handle With CompTIA Certifications
Data breaches are an integral part of the digital world. Commonly used workplace sources, like mobile and IoT devices, increase the likelihood of a data breach. A study by Varonis found that most companies leave data unprotected. Lack of proper cybersecurity practices makes them vulnerable to frequent data breaches. Organizations around the world implemented work-from-home policies during the pandemic, resulting in a dramatic uptick in employees collaborating using cloud-based software and using a URL shortener to streamline their communication
Moving forward, it will be crucial for companies to be adept against top cybersecurity threats. And cybersecurity training, certification, and bootcamps will become a part of their culture to successfully fight against malicious attacks. Now is the best time to begin a career in cybersecurity.
Top Cybersecurity Threats of 2021
The abrupt transition to remote work forced many companies to move to the cloud without proper cybersecurity procedures in place. With employees logging in through unsecured networks and home computers, cybersecurity threats increased exponentially. The Varonis report found that an average financial services employee accessed nearly 11 million files. In larger organizations, the number doubles to 20 million files open to all employees. That’s a lot of data susceptible to a breach or cybersecurity attack. The average cost of a financial services data breach is amongst the highest in any industry, $5.85 million.
According to IBM’s Cost of a Data Breach report in 2020, more than half of data breaches are caused by a malicious attack. On average, it takes 280 days for an organization to identify a cyberattack, costing the organization $3.86 million.
While large-scale data breaches are publicized, it is less common to hear stories of small businesses suffering the consequences of cyberattacks. CompTIA’s research report, Cybersecurity for Digital Operations, states that only 35% of IT staff rated their current cybersecurity as completely satisfactory. At a time when companies of all sizes are becoming aware of top cybersecurity threats and how to prevent them, this is the right time to start your cybersecurity career. There’s an ever-increasing demand for cybersecurity professionals.
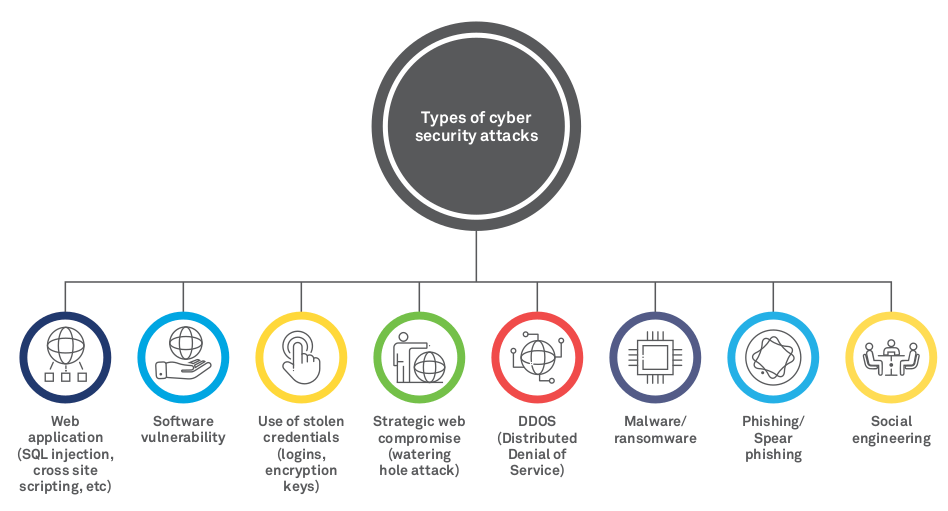
Source: Wipro
Before getting started, let’s look at common cyberattacks commonly affecting organizations.
1) Spoofing – The tactic of spoofing is commonly used in a cyberattack to disguise the source of attacking traffic. In simpler terms, spoofing is found when the source hides its true identity and poses as a reputable person or organization. For instance, sending an email with a fake “From:” address would be an example of spoofing.
2) DDoS – Although a hacker does not gain any valuable information from a Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack, they do create confusion and chaos. DDoS is an attempt to flood a website with traffic to overwhelm and render it unavailable.
Over time, the costs associated with DDoS attacks increase. A report by Corero found DDoS attacks cost enterprise organizations nearly $50,000, including downtime and mitigation costs.
3) Ransomware – This type of cyberattack holds files hostage. The hacker asks for a payment – mostly in an untraceable currency, such as Bitcoin in exchange for restoring data. Ransomware is the most common form of exportation. The more valuable the data, the more risk.
In July 2020, the University of Utah became the victim of a ransomware attack where they paid a $457,059.24 ransom.
4) Phishing – In phishing, the attacker sends mass emails to distribute malicious links or attachments. If opened, they can steal your login credentials and account information.
The worst part is that the email asks you to reset your password. Hackers take over your account and access your personal data when you attempt to comply.
According to the FBI, phishing was the most common type of cybercrime committed in 2020, and 43% of data breaches involved phishing.
5) Social Engineering – Social engineering is one of the most common ways for a hacker to get into your system. It involves human interactions where the perpetrators lie or manipulate their way into your organization to gain access to your systems. This is done under the disguise of something legitimate. Once they enter, the next step is installing malware to pull out confidential information.
In fact, 98% of all cyberattacks rely on social engineering, and 43% of IT professionals were targeted by social engineering schemes in 2020.
6) Tampering – In 2020, ransomware cases grew by 150% and 30,000 websites were hacked on a daily basis. Data tampering is defined as intentionally modifying, manipulating, or editing data through unsanctioned channels. It includes manipulating the URL, making it the biggest threat an application, program, or organization can face. To the unsuspecting visitor, the URL appears the same while the altered parameter allows hackers to access their information.
7) Exploiting the Back Door – In simple terms, a back door is a common application or program allowing remote access to a software, system, or network. In a cybersecurity attack, hackers install malware to steal data, deface a website, hijack a server, or launch a Distributed Denial of Server (DDoS) attack. In these attacks, remote file inclusion (RFI) is used. The referencing function is tricked into downloading a back door virus, or Trojan, from a remote host.
8) Malware – Malware includes several codes, bugs, and programs capable of confusing systems. They attack, destroy, or disable networks and devices. While malware does not cause permanent damage, it can manipulate data, change a system’s functions, and spy on user activity without authorization. In 2020, Marriott disclosed a security breach that affected the data of nearly 5.2 million guests. No organization, large or small, is immune to ransomware and malware attacks, which are growing more than 350% annually.
With the current rise of cybercrimes and vulnerabilities, organizations need to be proactive to protect their assets by hiring skilled cybersecurity professionals. The US Bureau of Labor Statistics predicts that cybersecurity jobs will increase 31% from 2019 to 2029, making it the fastest-growing field.
With more than 400,000 cybersecurity job openings, per Cyberseek, jobs that require cybersecurity certifications and skills continue to grow rapidly. Governments, Fortune 500 companies, and startups all value CompTIA as a cybersecurity certification authority.
How Can CompTIA Certifications Help You Handle Threats?
IT professionals and beginners interested in developing a career in cybersecurity, the CompTIA cybersecurity career pathway is a great choice. Certification proves to employers that you have the skills needed to protect their organization from cyberattacks and threats, giving you an edge over other candidates. Here are the cybersecurity certifications that can help you prepare for cyberattack prevention.
1) CompTIA Security+
To establish the foundational knowledge required in any cybersecurity role, the CompTIA Security+ certification is central. It acts as a bridge to advance you to intermediate-level cybersecurity jobs.
Performance-based questions emphasize the hands-on practical skills used by IT auditors, system administrators, network administrators, and security administrators.

Source: CompTIA
CompTIA Security+ validates these skills:
- Monitor and secure hybrid environments, such as cloud, mobile, and IoT
- Apply the laws and policies, risk and compliance, and principles of government
- Identify and analyze security events and incidents
- Assess an organization’s cybersecurity preparedness
- Recommend and implement security solutions
CompTIA Security+ certification will prepare you for these top jobs:
- Junior IT Auditor
- Penetration Tester
- Systems Administrator
- Network Administrator
- Security Administrator
CompTIA Security+ includes these modules:
- Module 1: Threats, attacks, and vulnerability
- Module 2: Technologies and tools
- Module 3: Architecture and design
- Module 4: Identity and access management
- Module 5: Risk management
2) CompTIA A+
CompTIA A+ is an entry-level cybersecurity certification recognized by organizations around the world. Certified professionals can solve cybersecurity problems related to networking, security, troubleshooting, and preventive maintenance.
This certification covers these skills:
- Identify, use, and connect hardware components and devices
- Explain types of networks and connections
- Install and configure laptops and other mobile devices
- Install and support operating systems (i.e., Windows, Mac, Linux, and mobile)
- Troubleshoot device and network issues
- Compare cloud-computing concepts and set up client side virtualization
- Troubleshoot PC and mobile device issues
- Identify and protect against security vulnerabilities for devices and their network connections
- Follow best practices for safety, environmental impacts, and communication and professionalism
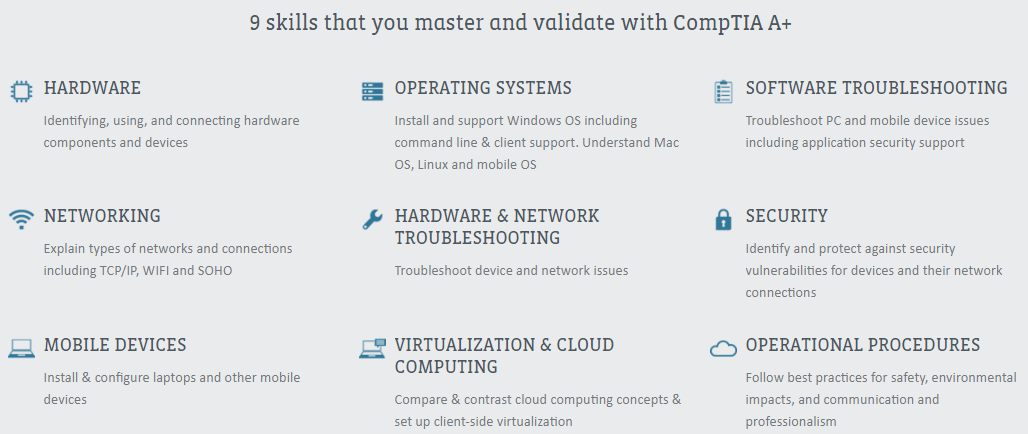
Source: CompTIA
Whether you’re in technical support or IT operations, CompTIA A+ certification helps jumpstart your cybersecurity career. CompTIA A+ certification prepares you for these jobs:
- Technical support specialist
- Helpdesk technician
- Field service technician
- System support specialist
- Data support technician
The 14 modules covered in the CompTIA A+ certification are:
- Module 1: IT professional soft skills
- Module 2: Safety for you and computer components
- Module 3: System component overview
- Module 4: Understanding motherboards
- Module 5: Understanding processors
- Module 6: Understanding types of memories
- Module 7: Understanding BIOS and CMOS
- Module 8: Hard drive and storage devices
- Module 9: Power supplies and voltage
- Module 10: Cables, ports, and connectors
- Module 11: Input and output devices
- Module 12: Managing printers
- Module 13: Mobile devices, multimedia, and laptop computers
- Module 14: Course assessment
3) CompTIA Network+
If you have basic entry-level experience in the IT field, you can take the CompTIA Network+ certification directly. In this training, you’ll gain experience in network administration, making you valuable in the IT field.

Source: CompTIA
CompTIA Network+ certification includes the following skills:
- Understand cabling, storage, and device technologies.
- Summarize common threats and physical device security, while protecting wired and wireless networks.
- Use tools to facilitate seamless performance and connectivity.
- Implement best practices to control the network, establish policies, and manage business continuity.
Top companies, including Dell, HP, and Apple, accept this certification globally. CompTIA Network+ will prepare you for these jobs:
- Junior network administrator
- Computer technician
- Helpdesk technician
- Network field technician
- Junior systems engineer
- IS consultant
- Network field engineer
- System engineer
- Network support specialist
- Network analyst
Numerous organizations have made CompTIA certifications mandatory for specific roles and the job postings list them as a primary requirement. With a CompTIA certification, you are more eligible for a job than non-certified candidates.
Prepare for Your Certification
Are you ready to start your career as a cybersecurity professional? The first step is to register for a relevant CompTIA certification training bootcamp. GreyCampus is an industry leader in providing cybersecurity training certifications including, CompTIA Security +, CompTIA A+, CompTIA Network+, and CISSP. These cybersecurity training programs are instrumental in advancing your cybersecurity career.
Want To Prevent Cybersecurity Threats? Join a Bootcamp Today!
