Focus on These 10 In-demand Skills to Land High-paying Cybersecurity Jobs
Do you know what the Toll Group, Marriott International, SolarWinds, Twitter, and Garmin had in common last year? They are among the many organizations that found themselves on the wrong end of a cyber-attack. Gone are the days when security breaches and cyber-attacks affected the data security of a few million users. Ransomware damages alone have risen from $325 million to more than $11.5 billion in 2019 globally. This year, the prediction is it will touch the $20 billion mark.
However, with the threat comes the protector. Hiring for cybersecurity jobs helps companies strengthen their IT controls and prepare them for future cyberattacks. Companies were expected to spend more than $1 trillion on cybersecurity products and services in five years ending this year. Services would also include the hiring of the services to fill cybersecurity jobs. There is one small problem, though. There aren’t enough qualified professionals to fill all the jobs in cybersecurity. The estimates are that as many as 3.5 million cybersecurity jobs are waiting to be filled at the moment. The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics expects a growth of 31 percent in this expertise, and cybersecurity jobs salary of up to $ 420,000 in the current market.
There is a massive, growing demand for these services, there is a dearth of talent, and there are highly positive predictions by experts about cybersecurity jobs. This means we can safely skip the part where we convince you why cybersecurity is a good career choice for you.
10 Skills That Count in Cybersecurity
Once you opt for a career in cybersecurity, you have to hone the skills that can make you a top pro in this field. Here are 10 cybersecurity skills that make sure your prospective employer is most likely to look for in you.
1) Application Development Security
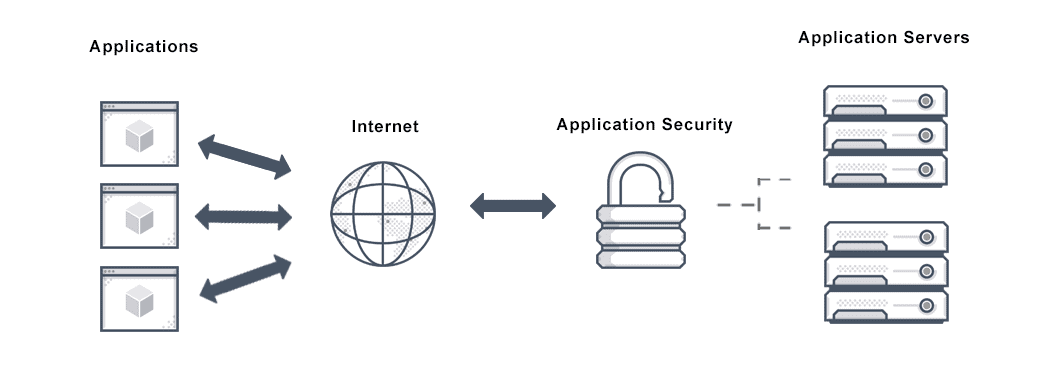
With this skill, you can detect security loopholes in applications and fix them by improving the security around them. Application development security is as important during the development stage as it is after deployment.
Source: AVI Networks
Applications are increasingly becoming a target for hackers. As a response, numerous tools and methods can apply to secure different application elements. These broadly fall into the category of security testing tools and application shielding products.
Tests have revealed that as many as 85 percent of applications have at least one security flaw that needs a fix. Common flaws include information leakage, cryptographic flaws, inferior code quality, inadequate input validation, credentials issues, and more.
Entry-level cybersecurity jobs may require the implementation of features like authentication, authorization, and encryption, apart from additional codes to reduce security threats.
2) Cloud Security
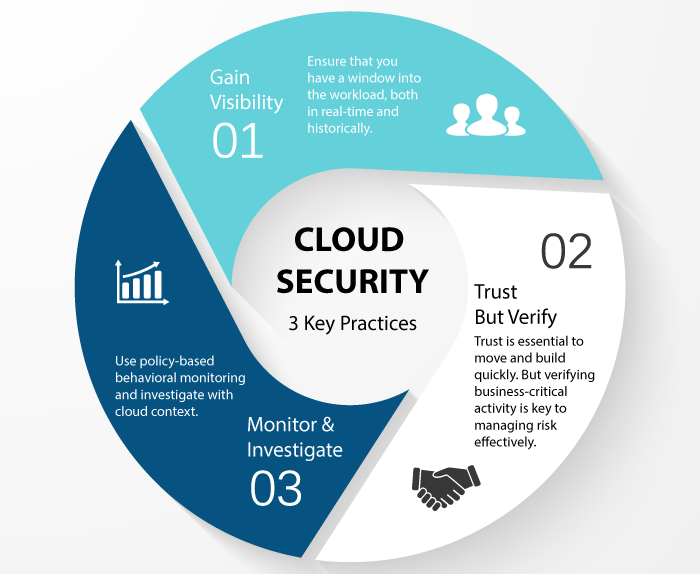
As a cybersecurity expert, you also need to secure your cloud-based information and database. To put a cloud security framework in place you will have to define policies and rules and use tools and configurations. You will have to administer the cloud security architecture, which will define the users and their permissions, sometimes through remote cybersecurity. The architecture will decide how to implement security controls to protect your cloud-based applications and network and data and user access.
Source: Threat Stack
Cloud security also involves the identification of security, compliance, and threat vulnerabilities to the cloud. You must ensure your policies meet industry compliance standards, as well. The offline security around devices and hardware linked to your cloud database also needs strengthening as a part of cloud security measures.
The National Institute of Standards and Technology identifies five essential pillars of cloud security. These are the identification of processes that need security risk assessments, protection of information in the event of an attack, detection of issues by monitoring systems, implementation of tools to respond to a threat, and restoration of cloud security after an attack.
3) Advanced Malware Protection
Advanced malware protection takes care of all the three basic facets related to malware. It includes prevention, response, and recovery from malware threats. This generation of malware protection has to address the issue of cloud-based cyber threats. In jobs in cybersecurity, you have to implement cloud-powered cybersecurity, faster deployment of remedies and response, and automated sandboxing.
Widely available commercially, advanced malware protection products will protect network entry points in all systems, devices, and network appliances. They can also help a network recover from breaches and intrusions. Minimizing the damage and blocking malicious files are actions that cybersecurity jobs involving advanced malware protection enable through retrospective alerting and remediation.
4) Security Information and Event Management (SIEM)

Source: ManageEngine
Security Information and Event Management is the bigger picture review of your organization’s information security. Often a part of cybersecurity entry-level jobs is to analyze log files for potential security threats and events. Analysts review data collected from log files in real-time to maintain visibility of the information systems at all times. The event management part, too, requires real-time monitoring of information systems to notify red flags to network administrators.
Cybersecurity experts generally put a SIEM tool in place that is configured to receive all event data. The sources of these data can be servers, operating systems, firewalls, malware protection tools, etc. You will be defining normal incidents and security incidents as a part of SIEM and setting the rules for reporting and alerts. Advanced SIEM practices can correlate a set of isolated data events into meaningful security issues.
5) Threat Intelligence
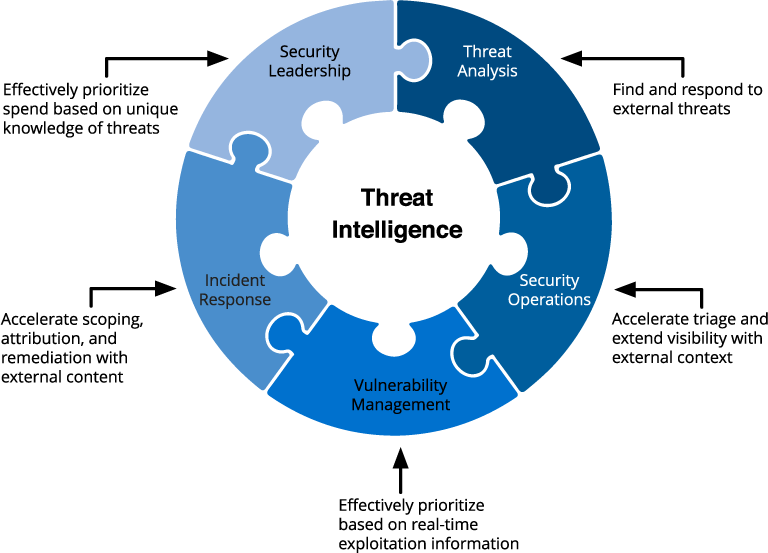
Threat intelligence believes in keeping your enemies closer, as the adage goes. It involves the collection, processing, and analysis of a threat and unravelling its underlying motive and pattern.
Source: OmniSci
Advanced persistent threats are a common phenomenon in cybersecurity, and threat intelligence helps you in preempting future attacks, and preparing for them. Cybersecurity entry-level jobs can have aspects of threat intelligence, like weaving the feeds from networks, IPS, security tools, and SIEM. However, advanced threat intelligence can go a step beyond and throw light on the malicious actors’ intent, behavior, technique, and process.
From the entry-level security analyst who identifies and addresses risks and threats to top management reviewing the organizational risks, threat intelligence has something for everyone. It does so by completing the data intelligence life cycle by converting raw data to meaningful intelligence.
6) DevSecOps
By inserting “Sec” in DevOps, cybersecurity jobs have a more prominent place in the IT business environment. DevSecOps aims to give due status to security at the same level as development and operations in terms of proficiency and prioritization.
All individuals across different technology domains participate in the applications development stages. With DevSecOps, security features embed at the development and iteration stage more seamlessly. In this continuous integration process, the cost of security and compliance drastically reduces, while the security features proactively integrate.
For a cybersecurity professional, designing and monitoring a DevSecOps environment efficiently means that applications and products not only get built faster but are also more robust from a security standpoint.
7) Security Incident Response
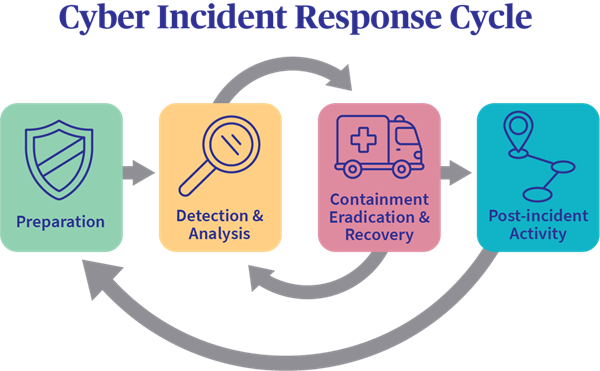
Security incident response picks up incidents and covers its entire lifecycle from identification till resolution through analysis and response. In case of a cyberattack or a data breach, this methodology activates to minimize the impact and accelerate the recovery process.
Source: AXA XL
As a part of the security incident response, experts carry out a thorough investigation of the incident to understand it better and be well-prepared to face the same or similar threats in the future. A well-developed security incident response prepares the cybersecurity expert to protect the company with a more prepared response in the future.
The response mechanism for entry-level cybersecurity jobs includes preparing for a security incident, identifying such incidents as they appear, and early containment of these incidents. Part of the response is also to neutralize the threat that an incident poses and ensure the business recovers fast from any damages. And as mentioned above, the lessons learned part of the security incident response improves the cybersecurity team’s response procedures.
8) Identity and Access Management
Cybersecurity jobs are not just about external threats and your preparation and response for them. Strengthening your internal security includes watertight measures in identification and access management. Accesses are potential entry points for data breach and attacks, so managing them efficiently is of utmost priority.
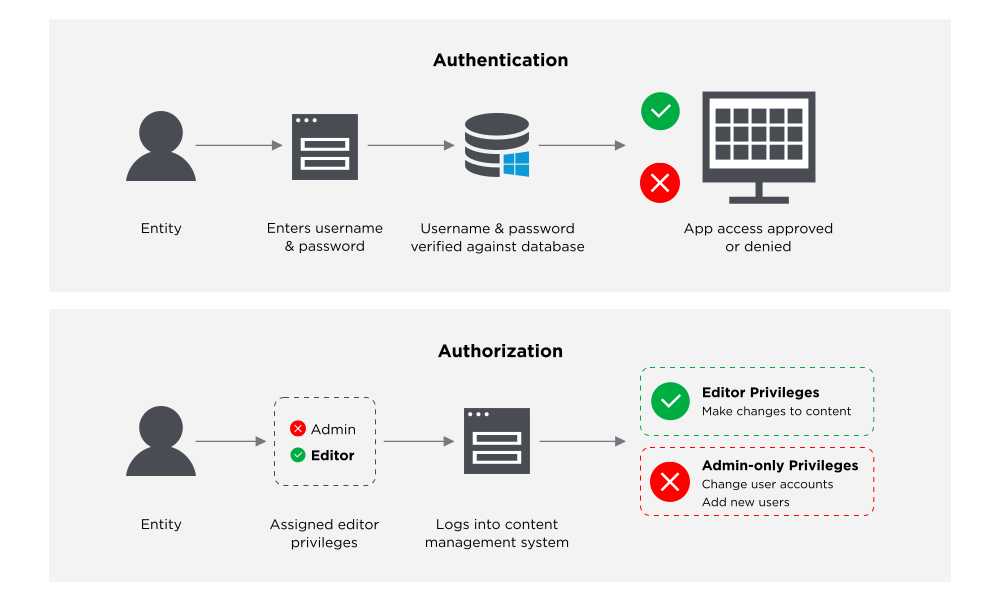
Source: Onelogin
As a cybersecurity expert, you have to put an identity and access management framework in place that controls the user access to critical databases and information. You will be defining the access levels and identifying the level a person falls under. You must also define a mapping of roles in the system so that you can add, delete, and update individual accesses as per their roles.
Corporate resources are crucial to the data privacy and confidentiality of an organization. The cybersecurity jobs experts should ensure they can define, maintain, and monitor user privileges at all times.
9) Digital Forensics
A niche skill within this domain, cybersecurity jobs salary for expertise in digital forensics have a promising future. You will collect, analyze, and archive all IT-related evidence to identify your network’s vulnerabilities. Your findings are crucial in developing mitigating mechanisms, as well as spotting nefarious activities. With advanced skills, you will also be responsible for devising counterintelligence strategies against potential hacks and breaches.
Organizations with large user bases, government sites, and leading financial institutions advocate the use of hypervigilance as a tool for cybersecurity. The use of digital forensics in such organizations is paramount.
10) Mobile Device Management
With the increasing use of handheld devices, with a variety of operating systems and service providers in them, mobile data management is now more important than ever for cybersecurity jobs.
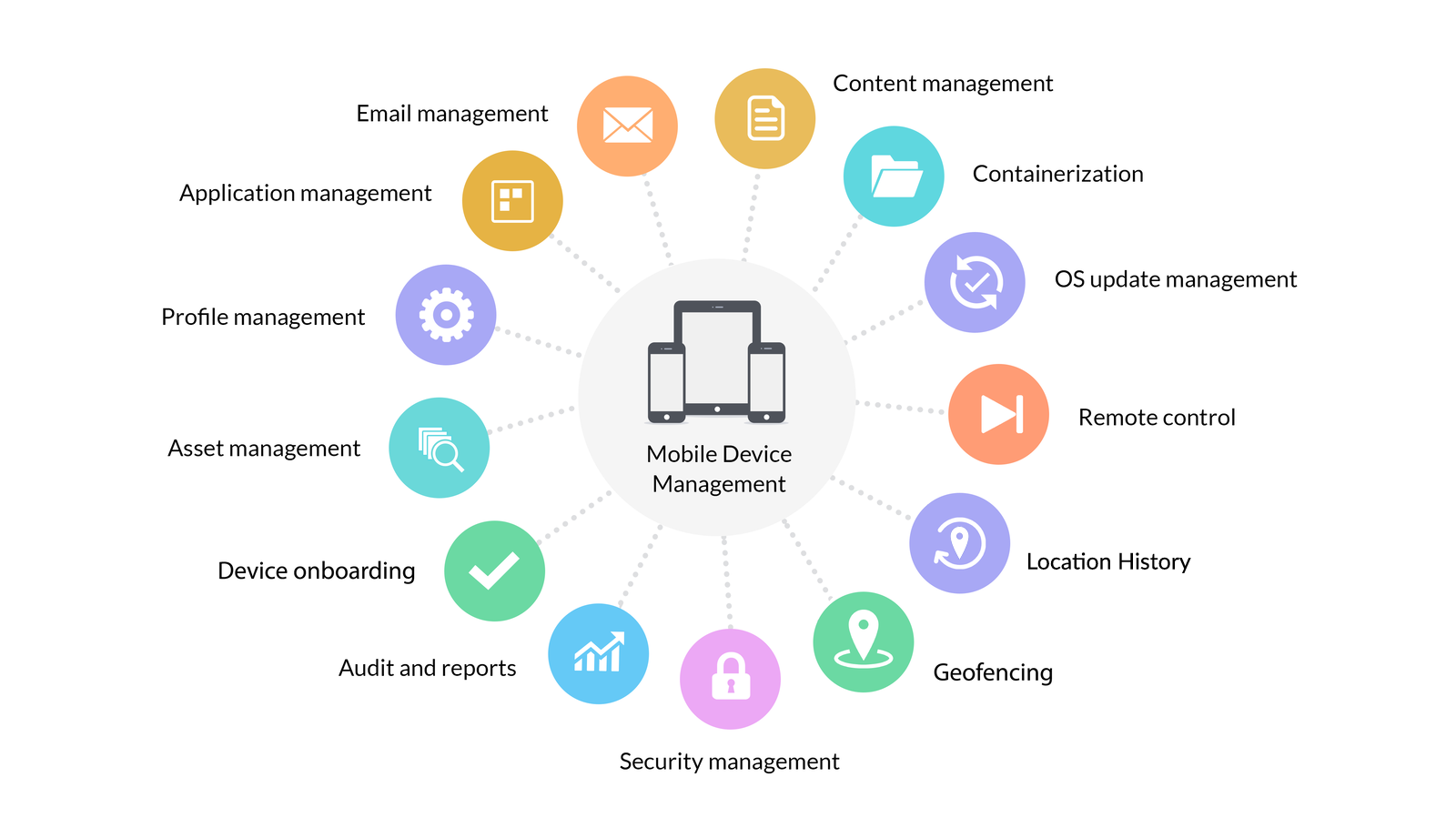
Source: ManageEngine
Businesses address the impact and context of device use through their enterprise mobility management mechanism, and mobile device management is a core component of it. Notably, mobile device management can include not just smartphones, but also laptops, tablets, and IoT devices. Central remote management makes remote cybersecurity jobs possible in this skillset, so devices can be detected in the corporate network and policies implemented through over-the-air commands. The primary aim remains the security of the corporate network and its coexistence amidst end-user-owned devices.
Most organizations would agree that what hackers and cybercriminals do is nothing less than an act of war. Their acts not only cost millions to the businesses and governments but also compromise the privacy of innocent users. As a cybersecurity expert, you become the weapon and the shield that protects netizens and enterprises from cyberattacks. As the first line of defense, you must have the equipment to put up a brave fight against these attacks.
GreyCampus cybersecurity jobs certifications offer industry-proven education and skillset through its four training programs. With a GreyCampus certification, you are better prepared to implement and maintain a robust cybersecurity environment in your workplace and businesses.
Want To Become a Cybersecurity Professional? Join a Bootcamp Today!